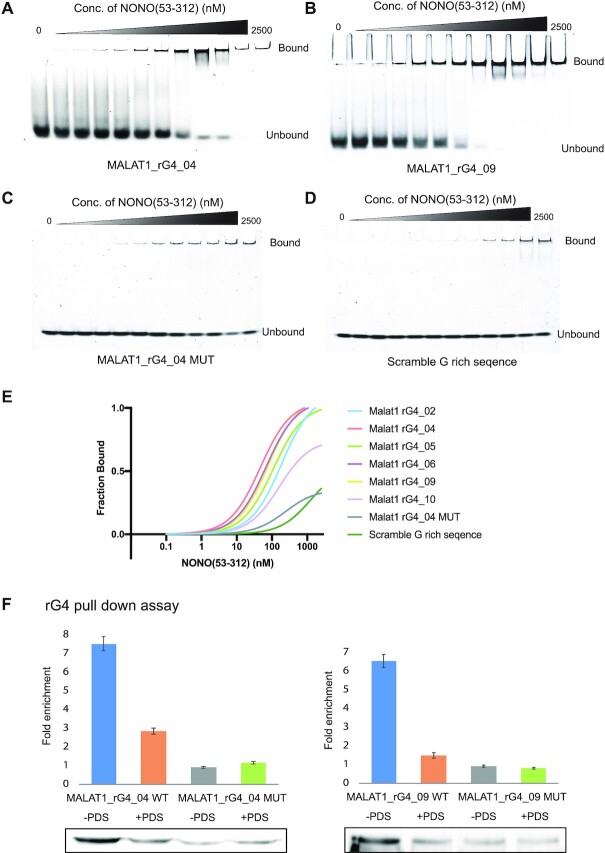
Figure 3.
MALAT1 rG4-NONO protein interactions in vitro and in nuclear lysate. (A) EMSA with recombinant NONO (53–312) and MALAT1 rG4_04. (B) EMSA with recombinant NONO (53–312) and MALAT1 rG4_09. (C) EMSA with recombinant NONO (53–312) and MALAT1 rG4_04 MUT. (D) EMSA with recombinant NONO (53–312) and scramble G-rich sequence. (E) Binding curves of recombinant NONO (53–312) and MALAT1 rG4_02, MALAT1 rG4_04, MALAT1 rG4_05, MALAT1 rG4_06, MALAT1 rG4_09, MALAT1 rG4_10, MALAT1 rG4_04 MUT and scramble G-rich sequence. The bindings of NONO to rG4s are stronger than rG4 mutant and scramble G-rich sequence, suggesting the binding is rG4-specific. (F) rG4 pull-down assay with HEK293T nuclear lysate. Western blot result of rG4 pulldown shows that NONO is enriched by MALAT1_rG4_04 and MALAT1_rG4_09 wildtype rG4s but not rG4 mutants, and the interaction can be disrupted by adding 20 μM PDS. In each blot, the rG4 mutant with no PDS treatment is normalized to one. Three independent experiments are performed. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (S.E.M.). The representative blot is shown here.