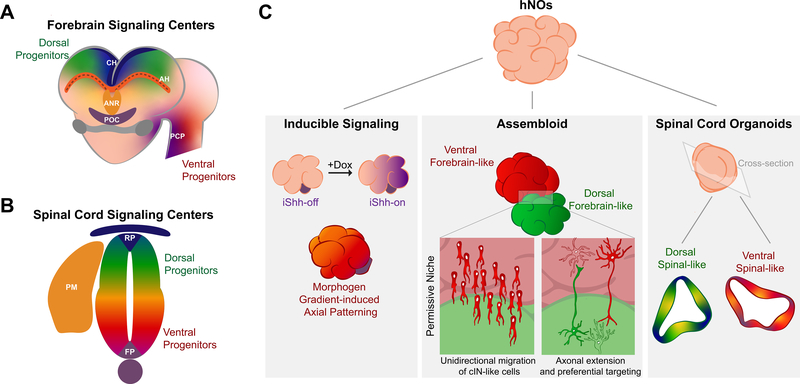
Figure 2. Signaling centers and assembloids.
(A) The developing vertebrate forebrain is patterned by multiple signaling centers including the anterior neural ridge (ANR), the cortical hem (CH), the prechordal plate (PCP), and the antihem (AH, at dorsal-ventral telencephalon boundary). (B) The developing spinal cord is patterned by multiple signaling centers including the roof plate (RP), the floor plate (FP), and paraxial mesoderm (PM). It contains both dorsal and ventral progenitors. (C) Human neural organoids (hNOs) can be bioengineered as assembloids that contain inducible signaling centers (e.g. inducible Shh (iShh) domains). Moreover, interregional phenomena like unidirectional migration of cortical interneuron (cIN)-like cells or axonal extension and preferential targeting may also be observed. In spinal cord organoids, exposure to select growth factors induces spontaneous emergence of both dorsal and ventral signaling centers that morphogenetically pattern adjacent organoid regions.