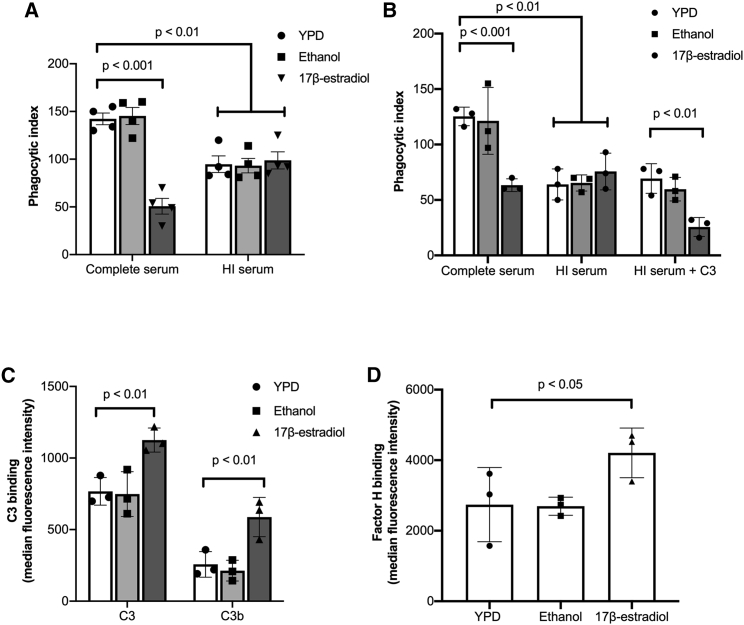
Figure 2.
Estrogen promotes innate immune evasion of C. albicans through the inhibition of opsonophagocytosis
(A) J774A.1 macrophages were maintained in either complete serum or heat-inactivated (HI) serum and infected with C. albicans pre-exposed to YPD, 0.3% ethanol, or 10 μM 17β-estradiol at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5.
(B) J774A.1 macrophages were maintained in either complete serum, heat-inactivated (HI) serum, or heat-inactivated serum supplemented with purified C3 and infected with C. albicans pre-exposed to YPD, 0.3% ethanol, or 10 μM 17β-estradiol at an MOI of 5.
(C) C. albicans was grown in YPD with or without 10 μM 17β-estradiol, incubated in human serum for 20 min, and fixed with 4% PFA, and C3 and C3b binding was quantified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS).
(D) C. albicans was grown in YPD with or without 10 μM 17β-estradiol, incubated in human serum for 20 min, and fixed with 4% PFA, and Factor H binding was quantified by FACS.
Data represent the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. Individual data points represent each independent biological replicate. See also Figure S2.