Figure 5.
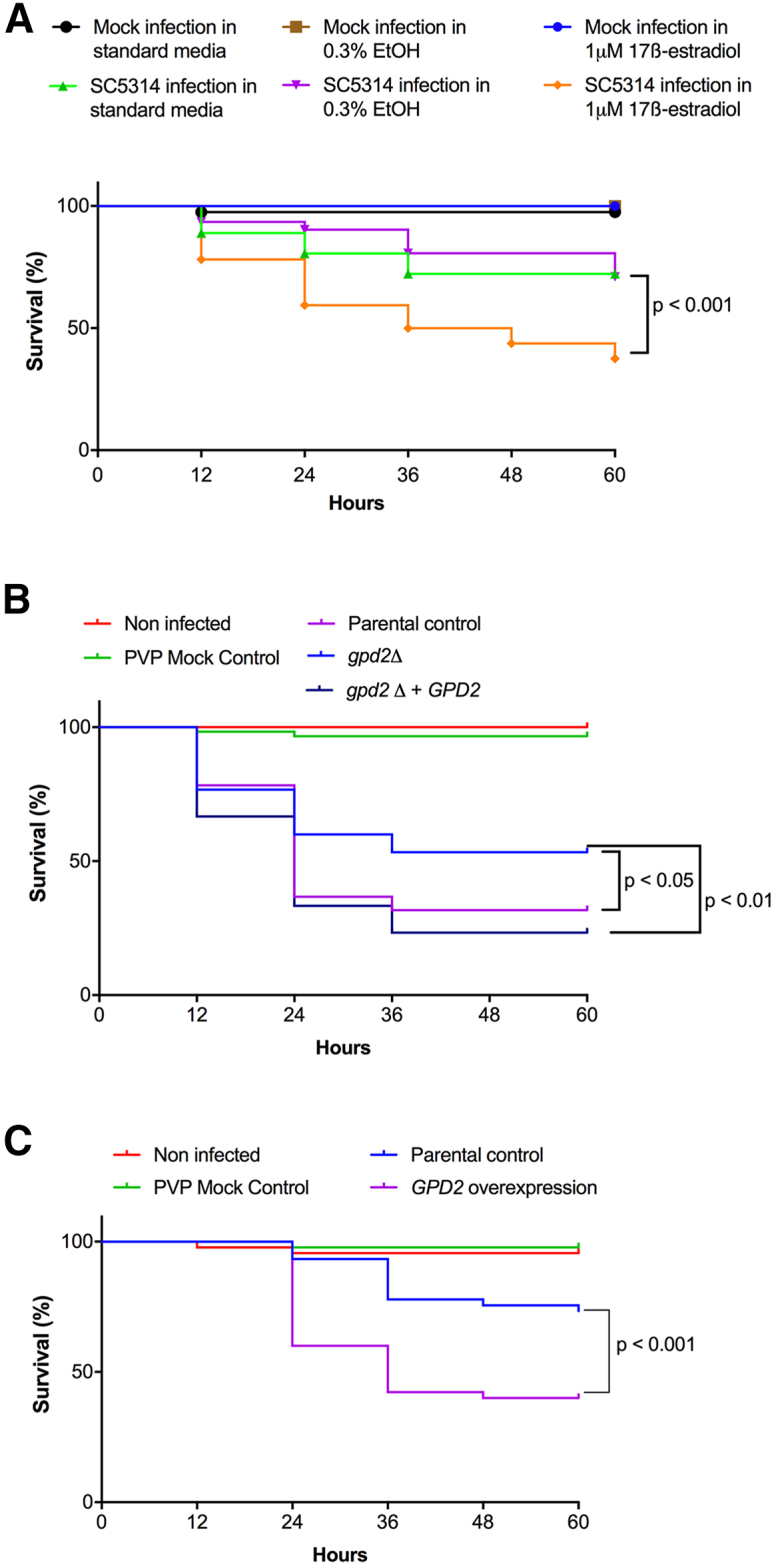
Estrogen promotes the virulence of C. albicans in a zebrafish larval infection model
(A) C. albicans (SC5314) was microinjected into the hindbrain ventricle of zebrafish larvae in the Prim25 stage. Infected larvae were maintained in E3 medium, or E3 medium supplemented with 0.3% ethanol, or 1 μM 17β-estradiol, and larval survival was monitored every 24 h until day 5 post fertilization.
(B) The parental control (SN250-CIP30), gpd2Δ mutant (gpd2Δ-CIP30), and reconstituted control (gpd2Δ-CIP30-GPD2) strains were microinjected into the hindbrain ventricle of zebrafish larvae in the Prim25 stage. Larvae were maintained in E3 medium and larval survival was monitored every 24 h until day 5 post fertilization.
(C) The parental control (CAI4-pSM2) or GDP2 overexpression (CAI4-pSM2-GPD2) strains were microinjected into the hindbrain ventricle of zebrafish larvae in the Prim25 stage. Larvae were maintained in E3 medium and larval survival was monitored every 24 h until day 5 post fertilization.
The survival curves represent data pooled from three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences were determined by the log rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
