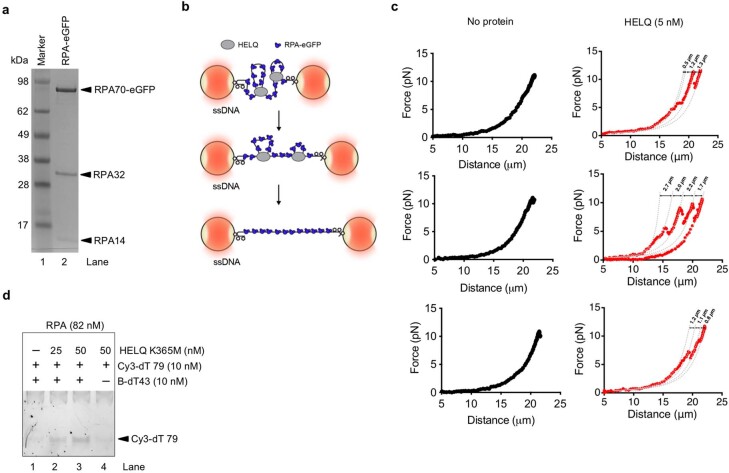
Extended Data Fig. 8. HELQ can capture non-complementary DNA strands in presence of RPA.
a, SDS-PAGE gel (4-12%) showing purified recombinant human RPA–eGFP from E. coli. The gel was stained with CBB. Single preparation of RPA–eGFP used in this study. b, A schematic of DNA pulling process. RPA–eGFP-coated ss-λ DNA tethered between the two streptavidin beads (~4.8 μm diameter) was collapsed by bringing beads at <5 μm distance. Beads were subsequently pulled apart at constant speed (step size = 0.2 μm, frequency = 500 Hz). Force-extension curves were then recorded. c, Force-distance curves of individual eGFP-RPA-coated ss-λ DNA molecules recorded in the absence or presence of HELQ (left and right panels, respectively). Sawtooth-like patterns in the FD curves (red) indicate disruption of ssDNA loops held together by HELQ. The average loop sizes (1.5 ± 0.5 μm, N = 10) were estimated from the differences in the fitted contour lengths between the disruption events (dashed lines). d, Native gel showing the capture assay with the indicated concentrations of HELQ(K365M) in the presence of RPA (82 nM). The experiment performed two times with similar results.