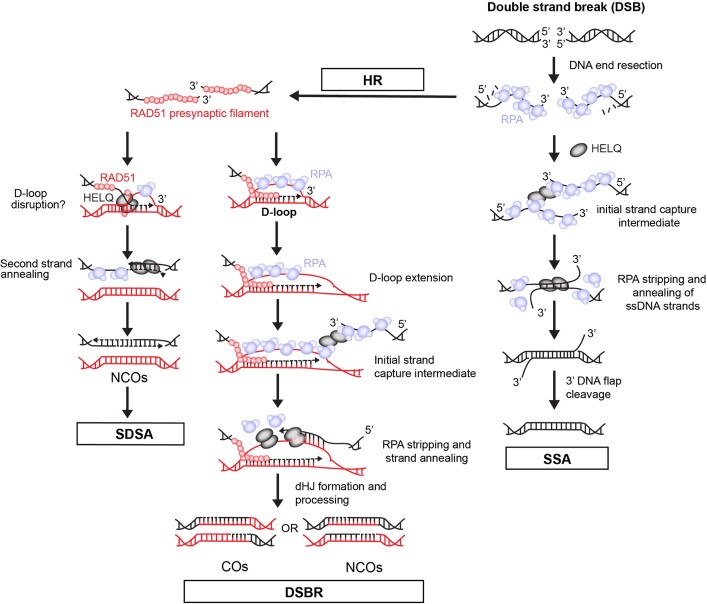
Extended Data Fig. 10. A possible mechanism of HELQ function in HR and SSA.
HR, In HR, following DSB, 5′ DNA ends are resected by nucleases, which generates RPA-coated 3′ overhangs. RPA is displaced by RAD51 giving rise to presynaptic nucleoprotein filament formation. This RAD51-filament invades homologous DNA duplex through its 3′ end. DNA invasion result in D-loop formation, which is extended by DNA synthesis. If the SDSA pathway is invoked, HELQ can disrupt the D-loop to displace and/or anneal the extended strand with the broken duplex via its helicase and strand annealing activities. Alternatively, in DSBR, the D-loop can be greatly extended and RPA-coated DNA strands in D-loop and second 3′ overhang can be captured by HELQ. During this second-end capture step, HELQ strips RPA from ssDNA and anneals complementary DNA strands together to prime DNA synthesis, restoring the broken DNA and resulting in either crossover or non-crossover products. SSA, similar to HR, longer RPA-coated 3′ overhangs can be captured by HELQ. Post capture, HELQ strips RPA from both ssDNAs and actively anneals the DNA strands together using base-pairing. The remaining flaps are cleaved, and nicks are ligated by specific nuclease and ligases completing the DSB repair reaction.