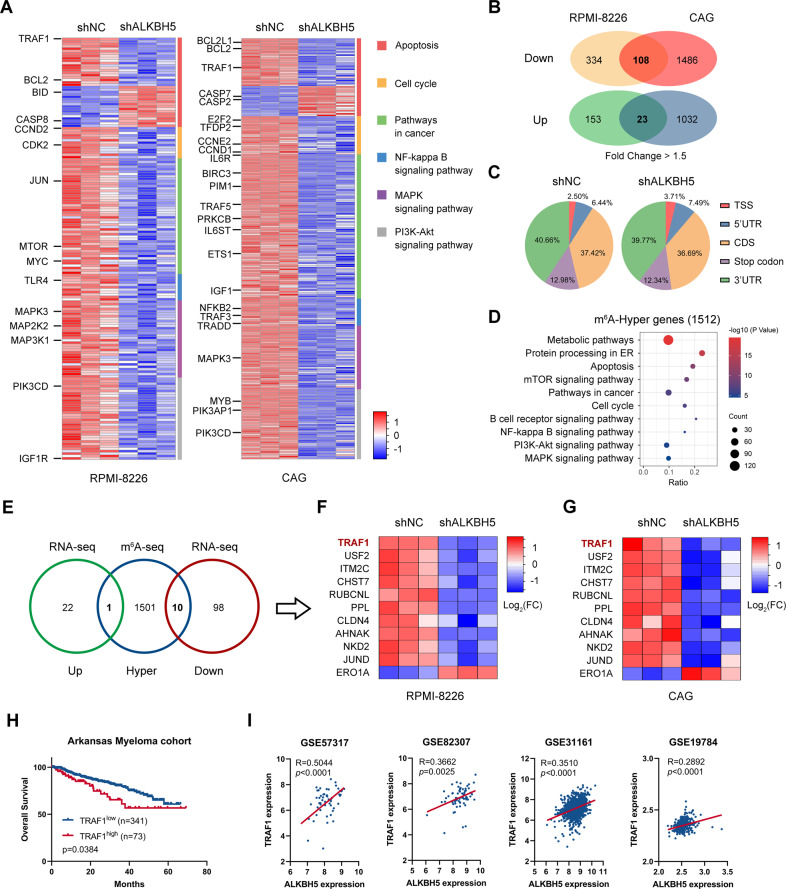
Fig. 5. Identification of potential downstream targets of ALKBH5 in MM cells.
A, B RNA-seq analysis of MM cells upon ALKBH5 KD. Heatmap (A) shows differential expression of indicated KEGG pathway genes in RPMI-8226 (left panel) and CAG (right panel) upon ALKBH5 KD. Venn diagram (B) shows the number of genes with significant changes in expression (fold change > 1.5) upon ALKBH5 KD in RPMI-8226 and CAG cells. C, D m6A-seq analysis of ALKBH5 KD in RPMI-8226 cells. Distribution of total m6A peaks in the indicated regions of mRNA transcripts in the control and ALKBH5 KD cells (C). Bubble plot (D) shows KEGG pathway analysis of the genes with significantly increased m6A abundance in ALKBH5 KD cells (P < 0.05). E Integrative analysis of RNA-seq and m6A-seq to identify the potential targets of ALKBH5 in MM. Up or Down indicates genes with significantly increased or decreased expression upon ALKBH5 KD in both RPMI-8226 and CAG cells as detected by RNA-seq (fold change > 1.5), respectively. Hyper indicates genes with significantly higher m6A abundance in m6A-Seq (P < 0.05). F, G Heatmap shows differential expression of overlapped genes in RMPI-8226 (F) and CAG (G) upon ALKBH5 KD. H Kaplan–Meier survival analysis in the Arkansas myeloma dataset [31]. The cutoff value was determined by the maximum standardized log-rank statistic. P-value was detected using the log-rank test. I Pearson’s correlation between ALKBH5 and TRAF1 mRNA expression in the indicated datasets [35–38]. The expression values were log2 transformed.