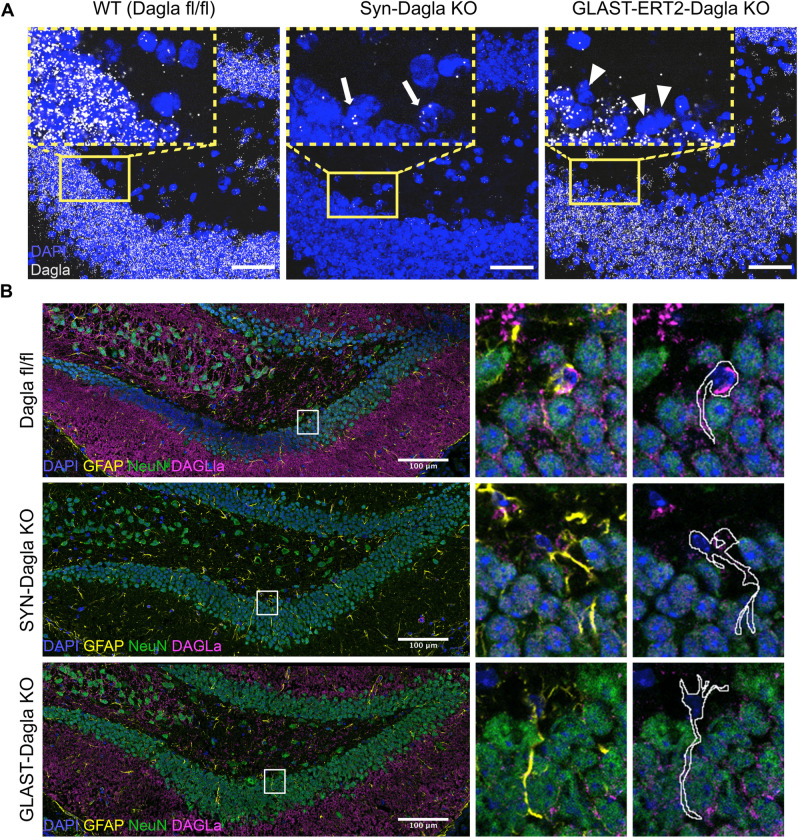
Figure 3.
Dagla is deleted in the progenitor-containing subgranular zone (SGZ) in GLAST-CreERT2-Dagla KO but not in Syn-Dagla KO mice. (A) Representative images of an RNAscope in situ hybridisation assay detecting transcripts of Dagla (white) in the DG in the hippocampus of Dagla fl/fl control, Syn-Dagla KO and GLAST-CreERT2-Dagla KO mice. Dagla is deleted in the neuronal granular cell layer in Syn-Dagla and in the progenitor-containing subgranular zone (SGZ) in GLAST-CreERT2-Dagla KO mice (scale bar 50 µm). The magnified insets (scale bar 10 µm) show SGZ with white arrows indicating Dagla expressing cells in Syn-Dagla KO and white arrowheads Dagla-negative cells in GLAST-CreERT2-Dagla KO mice in the NSC layer (n = 3–4 animals per group). (B) Immunostaining detecting DAGLa (magenta) co-localization with GFAP (yellow) and NeuN (green). The magnified insets show examples of GFAP-positive cells with NSPC morphology delineated with white. Progenitors express DAGLa in Dagla fl/fl control and Syn-Dagla KO SGZ and but not in GLAST-CreERT2-Dagla KO. NeuN positive neurons in granule cell layer express DAGLa in control and GLAST-CreERT2-Dagla KO sections, but not in Syn-Dagla KO (scale bar 10 µm).