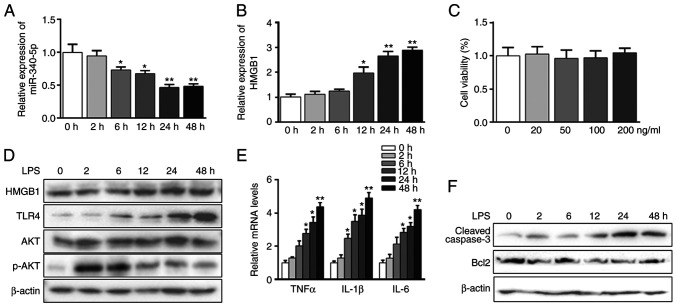
Figure 1.
LPS-induced acute inflammation and apoptosis parallels with miR-340-5p suppression and HMGB1 elevation in pancreatic acinar cells. (A) Pancreatic acinar cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for different durations. The expression level of miR-340-5p was assessed via RT-qPCR. (B) Pancreatic acinar cells were treated with of LPS (100 ng/ml) for different durations. The expression level of HMGB1 was assayed via RT-qPCR. (C) Cell viability assay results: pancreatic acinar cells were treated with various doses of LPS for 48 h. (D) Pancreatic acinar cells were treated with LPS for different durations. The protein expression levels of HMGB1, TLR4, AKT and p-AKT were assayed via western blotting. β-actin was used as a control. (E) Pancreatic acinar cells were treated with LPS for different durations. The mRNA expression levels of TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6 were assayed via RT-qPCR. (F) Pancreatic acinar cells were treated with LPS for different durations. The expression levels of cleaved-caspase3 and Bcl2 were examined via western blotting. β-actin was used as a control. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. 0 h. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; TLR, Toll-like receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; p-, phosphorylated; miR, microRNA.