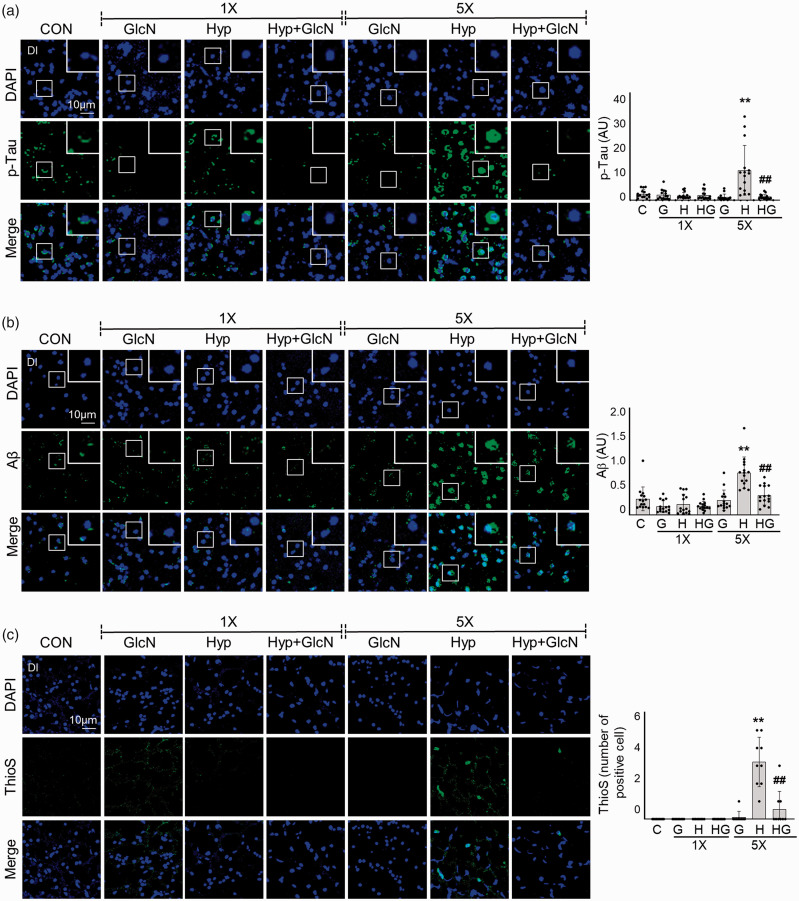
Figure 7.
SH- or RH-induced accumulations of Aβ and p-Tau deposition and plaque formation with or without GlcN pretreatment. Zebrafish were exposed to SH (1×) or RH (5×) with or without intraperitoneal pre-injection of GlcN (200 μg/g) at 2 h prior to each bout of hypoxia. Brain sections from representative Dl regions of control, SH, and RH zebrafish were processed for immunocytochemistry using anti-p-Tau (a, green) or -Aβ (b, green) antibodies or Thioflavin S (ThioS; c, green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The utilized anti-Aβ antibodies were specific for the C terminus of Aβ42. Enlarged images are presented in the white boxes. Graphs represent densitometric quantification of green images of p-Tau, Aβ, or This (n=3–5/group). Statistical analysis was carried out by Kruskal-Wallis with false discovery rate (FDR) multiple comparison test. (**p<0.01 vs. Cont, ##p<0.01 vs. SH or RH.)