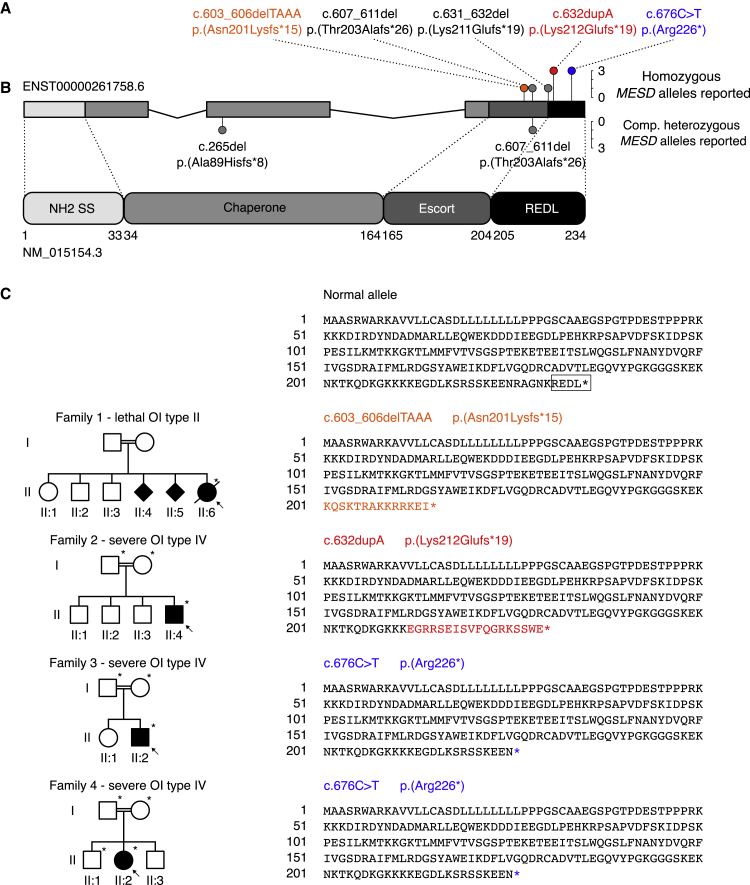
Figure 2.
Structure of the MESD gene and MESD protein, pedigrees of the described families, and representation of the mutant allele sequences
(A) The MESD gene consists of 3 exons (4,200 bp) and comprises 14.07 kb on chromosome 15. The cumulative frequency of the six known pathogenic MESD alleles (both this and two previous studies14,15) are denoted with colored lollipop graphs. The pathogenic alleles included in this report are highlighted in orange, red, and blue, respectively.
(B) Full-length MESD protein consists of 234 amino acids (aa) and contains 4 functional domains.
(C) Pedigrees of the 4 families with MESD variants and representation of the WT and mutant alleles. The proband in each family is indicated by an arrow. Filled circles, squares, or diamond structures represent individuals with OI. Individuals who were studied in each family are noted with asterisks. The variants in families 1 and 2 cause frameshifts and introduce premature termination codons 15 and 19 codons downstream of the frameshifts, respectively, and the variant in families 3 and 4 changes an asparagine residue to a stop codon, resulting in premature termination. All three variants cause the loss of the C-terminal REDL ER-retention sequence (marked with a square in the WT allele) needed for retrieval from the Golgi, and their position and mutant AA sequence is highlighted in orange, red and blue, respectively (matching colors in A).