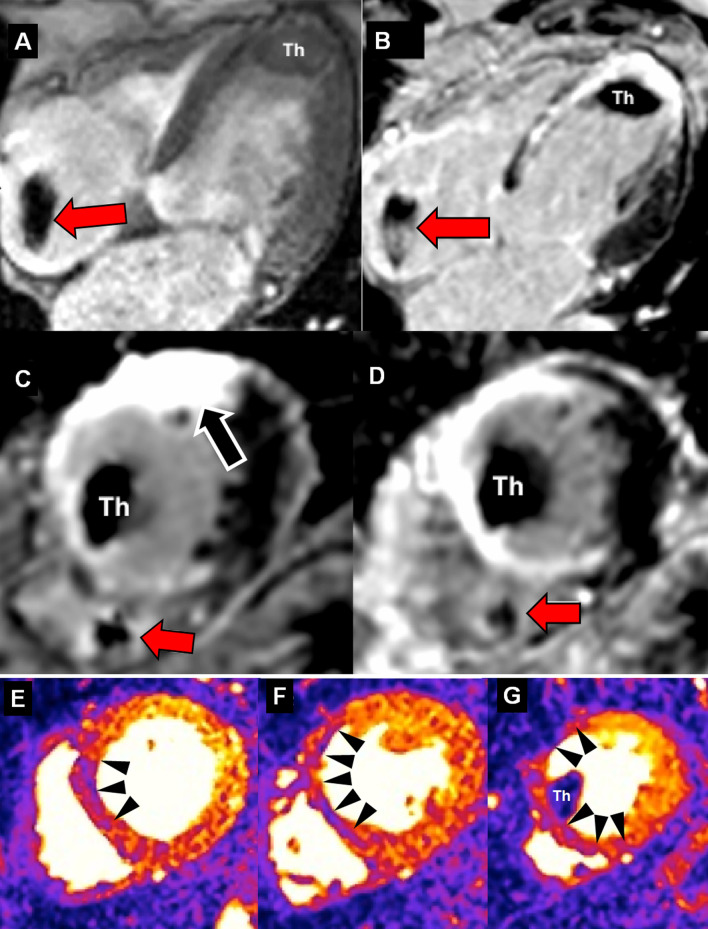
Fig. 3.
Stress perfusion-CMR in a PPM dependent patient. 67-year-old with known an antero-septal myocardial infarction, was referred to stress perfusion CMR to exclude myocardial ischemia after implantation of a MR-conditional implantable cardiodefibrillator (ICD) for primary prevention. A Cine fast-gradient echo acquisition of a 4-chamber view demonstrating a mural thrombus (Th) in the apex and the artifact of the ICD electrode (red arrow). B Corresponding standard phase sensitive inversion recovery (PSIR) 4-chamber view with visualization of the post-infarct scar in septal and apical segments as well as the apical thrombus (Th) and the ICD electrode (red arrow). Standard short-axis PSIR in C (with bandwidth of 140 Hz/pixel) and PSIR with increased bandwidth in D (300 Hz/pixel) to eliminate the ICD-related artifact on the anterior wall (black arrow in C), electrode (red arrow). The mural thrombus (Th) and the antero-lateral scar is visualized. E/F/G: Myocardial perfusion upslope maps of motion-compensated perfusion images in the basal (E), mid-ventricular (F) and apical (G) slices. Visualization of hypoperfused scar (black arrow heads) thereby excluding ischemia in this patient. Hypoperfusion of the mural thrombus in G (Th)