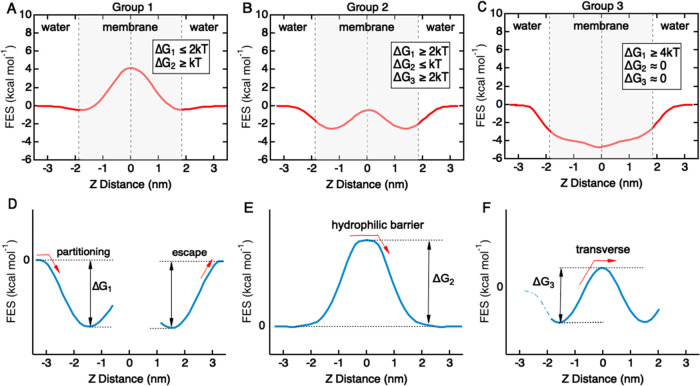
Figure 3.
Characterizing free-energy surface profiles for BBB translocation for the solute library. (A) Group 1 solutes have an energy barrier located in the hydrophobic core in the center of the bilayer (ΔG2 ≥ kT). In some cases, there are energy minima located in the head group regions, with a barrier to escape from the bilayer (ΔG1 ≤ 2kT) and an energy barrier between the two minima (ΔG3 ≤ kT). (B) Group 2 solutes have two energy minima located in the head group regions of the bilayer separated by a small energy barrier in the hydrophobic core. This profile results in a barrier to escape from the bilayer ΔG1 ≥ 2kT and an energy barrier associated with hopping between the two minima in the hydrophobic core (ΔG3 ≤ kT). (C) Group 3 solutes have an energy minimum in the center of the bilayer, resulting in a barrier to escape from the bilayer (ΔG1 ≥ 4kT). (D) Energy minima in the head group regions result in an energy barrier to escape from the bilayer (ΔG1). (E) Energy barrier in the center of the bilayer provides an energy barrier to translocation across the hydrophobic core (ΔG2). (F) Energy minima in the head group regions combined with an energy barrier in the center of the bilayer result in an energy barrier for hopping between the energy minima (ΔG3).