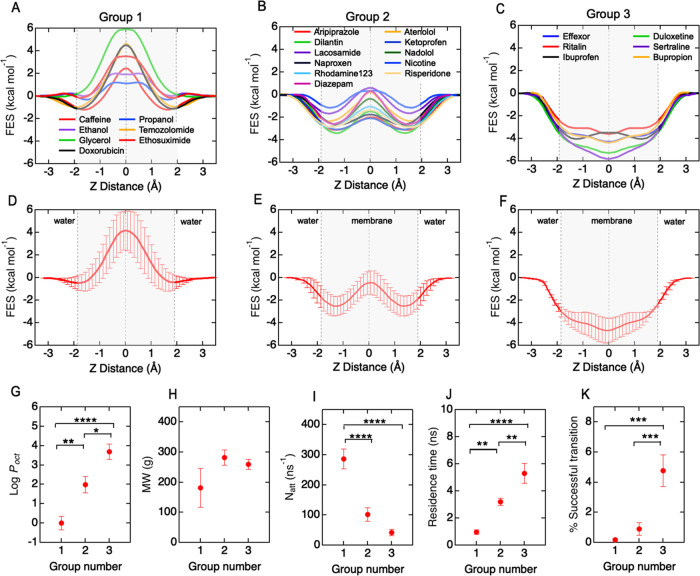
Figure 4.
Free-energy surface profiles, translocation kinetics, and physicochemical properties of a 24 solute library. Free-energy surface (FES) profiles can be classified into three groups based on energy barriers ΔG1, ΔG2, and ΔG3. (A) Group 1: ethanol, propanol, caffeine, glycerol, doxorubicin, ethosuximide, and temozolomide. (B) Group 2: nicotine, atenolol, diazepam, nadolol, lacosamide, abilify, risperdal, rhodamine-123, dilantin, ketoprofen, and naproxen. (C) Group 3: ibuprofen, effexor, ritalin, sertraline, duloxetine, and bupropion. (D–F) Average free-energy surface profiles for each group. (G–K) Dependence of hydrophobicity (log Poct), molecular weight, attempt frequency for bilayer entry, residence time in the bilayer, and the fraction of successful translocation events for each group. Bars represent mean ± standard error (SE). Statistical significance was tested with an ANOVA test with a posthoc Tukey test. Symbol meaning, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001.