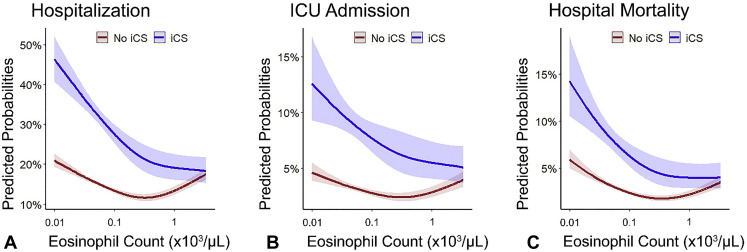
Figure 1.
Predicted probabilities of coronavirus disease 2019–related (A) hospitalization, (B) admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), and (C) hospital mortality as a function of baseline peripheral blood absolute eosinophil count (AEC), stratified by inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) use. These interaction plots show that the association between coronavirus disease 2019–related outcomes and AEC depends on the use of ICS (all P values for interaction < .001). The probabilities were calculated by fitting a logistic regression using a restricted cubic spline function for the AEC (log10-transformed). The 95% confidence intervals are indicated by the shaded area around the fitted line.