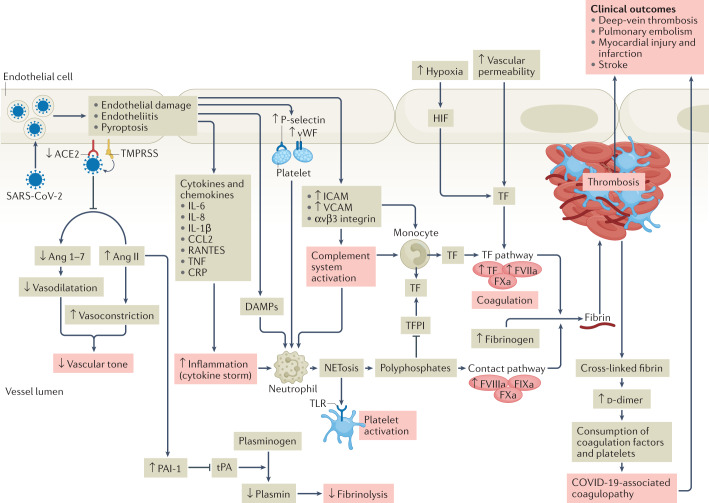
Fig. 1. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated coagulopathy.
Following entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) into the host endothelial cell by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, the expression and enzymatic activity of ACE2 are reduced, resulting in increased vascular permeability and tissue factor (TF) expression in subendothelial cells, as well as in leukocytes and platelets, which triggers coagulation. ACE2 can exert antithrombotic effects through various mechanisms, including the renin–angiotensin pathway, in which angiotensin I is converted by angiotensin-converting enzyme to angiotensin II (Ang II), which is then broken down by ACE2 to angiotensin 1–7 (Ang 1–7). Reduction in the expression of ACE2 leads to an increase in the level of Ang II, which stimulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) in various cells, including smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells and adipocytes. The increase in PAI-1 levels results in hypofibrinolysis. Endothelial cell activation or dysfunction results in a generalized inflammatory state, characterized by high levels of inflammatory cytokines, release of von Willebrand factor (vWF) and increased endothelial cell-surface expression of adhesion molecules such as P-selectin, promoting thrombus formation and leukocyte recruitment. Inflammation is an important driver of thrombosis, through several mechanisms. Inflammatory cytokines and viral-specific Toll-like receptors (TLRs) induce TF expression in monocytes, resulting in activation of the coagulation cascade. Platelet activation by TLR signalling results in increased platelet reactivity and platelet aggregation. Activation of neutrophils results in the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETosis), leading to activation of coagulation and providing a scaffold for the adhesion of platelets, red blood cells and platelet-adhesion molecules. In parallel, activation of coagulation via TF also results in thrombin generation and the formation of fibrin, which allows crosslinking of platelets and other cellular constituents and results in occlusive thrombus formation. CCL2, CC-motif chemokine 2; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CRP, C-reactive protein; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; FIXa, activated factor IX; FVIIa, activated factor VII; FVIIIa, activated factor VIII; FXa, activated factor X; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; RANTES, regulated on activation, normal T expressed and secreted; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TMPRSS, transmembrane serine protease 2; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule.