Figure 1.
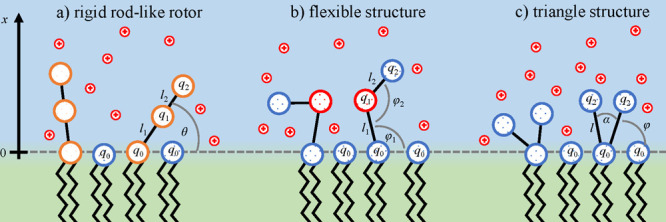
Schematic representation of the lipid monolayer in contact with the aqueous solution. Mobile ions are point-like charges and are represented by small red circles in the sketch. The monolayer is composed of two types of lipids. The first components are structured lipids with spatial charge distribution. We consider three cases: (a) rigid rod-like, (b) flexible segments, and (c) triangular head groups. The other component of the monolayer is a lipid that has its head group treated in a simplified manner, as only a point-like charge, and is expressed through the mole fraction of lipids in monolayer as β. It contributes to the overall charge density of the interface. In all cases of structured lipids, the first segment is immobile, lies in the plane x = 0, and has the charge number q0. Other segments protrude into the aqueous solution and possess certain degrees of freedom (see Model and Methods). Structures represent actual lipids, see Figure 2.
