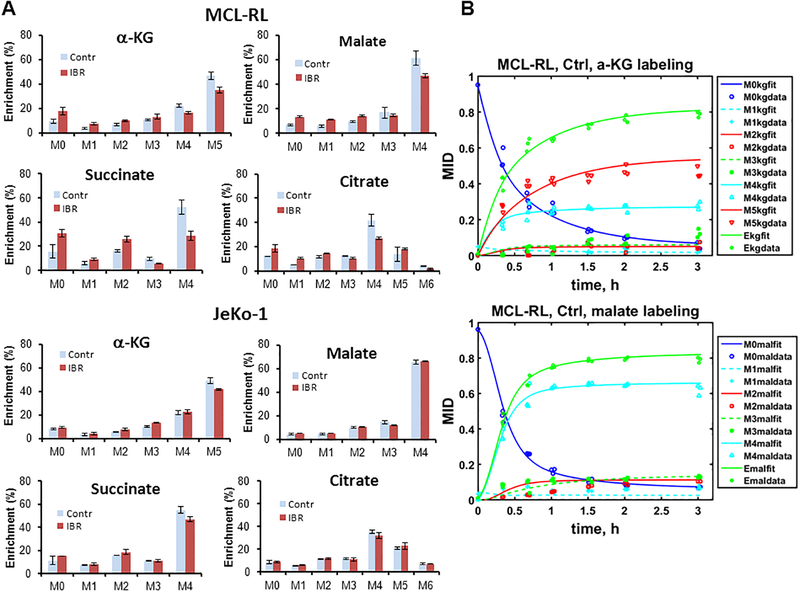
Figure 4. 13C LC-MS metabolomics with [U-13C5, U-15N2] glutamine tracer.
(A) MCL-RL and JeKo-1 cells were labeled with [U-13C5, U-15N2] glutamine for 8 h. Mass isotopologues of α-ketoglutarate, malate, succinate and citrate are shown. Isotopologue information of other metabolites such as aspartate, glutamate, oxaloacetate, pyruvate and lactate was also obtained (data not shown). α-Ketoglutarate is initially labeled at M+5 by glutaminolysis and reductive carboxylation. Then it is labeled at all isotopologues of M+1 through M+5 after multiple scrambling in the TCA cycle and exchange of molecules between mitochondrion and cytosol. Succinate and malate are initially labeled as the M+4 isotopologue then labeled as other isotopologues as well after network scrambling. Citrate in the cytosol is initially labeled as the M+5 isotopologue after conversion from M+5 α-ketoglutarate. Citrate in the mitochondrion and cytosol are initially labeled as M+4 and M+5 isotopologues. The M+4 citrate is from the first turn of TCA cycle (clockwise), and the M+5 citrate is from the direct conversion from the α-ketoglutarate due to mitochondrial or cytosolic reductive carboxylation. Then the labeled carbons are distributed to other isotopologues after multiple turns of TCA cycle and scrambling through other pathways and exchange of the metabolites between mitochondrion and cytosol. For example, M+6 citrate in this figure suggests incorporation of labeled carbons from pyruvate produced in the multiple pathways including various pyruvate cycling routes (examples can be seen in Fig. S1). (B) MCL-RL and JeKo-1 cells were incubated in the [U-13C5, U-15N2] glutamine containing medium and collected at multiple time points for time course LC-MS analysis of the metabolite mass isotopologue fractions. The time course labeling of α-KG and malate along with fitting to the fragmented mass isotopomer model is presented. Ekg = (M1 + 2M2 + 3M3 + 4M4 + 5M5)/5; average enrichment of α-KG. Emal = (M1 + 2M2 + 3M3 + 4M4)/4; average enrichment of malate. Reversibility was assumed for all the reactions in the TCA cycle except for the reaction from oxaloacetate to citrate (Fig. S1). Data in Fig 4A were presented as mean±SD.