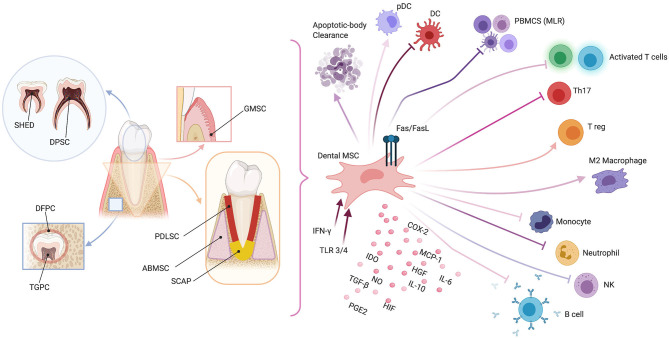
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of dental mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) sources (left panel) and possible immunomodulating mechanisms (right panel). Dental pulp MSCs (DPMSCs), MSCs from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (MSCHEDTs), periodontal ligament MSCs (PDLMSCs), alveolar-bone derived MSCs (ABMSCs), gingival MSCs (GMSCs), MSCs from apical papilla (MSCAPs), dental follicle progenitor cells (DFPCs), and tooth germ progenitor cells (TGPCs). Peripheral blood mononucleated cells (PBMCS), mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR), plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC), natural killer (NK), type-2 cyclooxygenase (COX2), Fas ligand (FasL), indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), nitric oxide (NO), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), hypoxia-induced factor (HIF), interleukins 6 and 10 (IL6 and IL10, respectively), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), Toll-like receptor (TLR), and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). Created with BioRender.com.