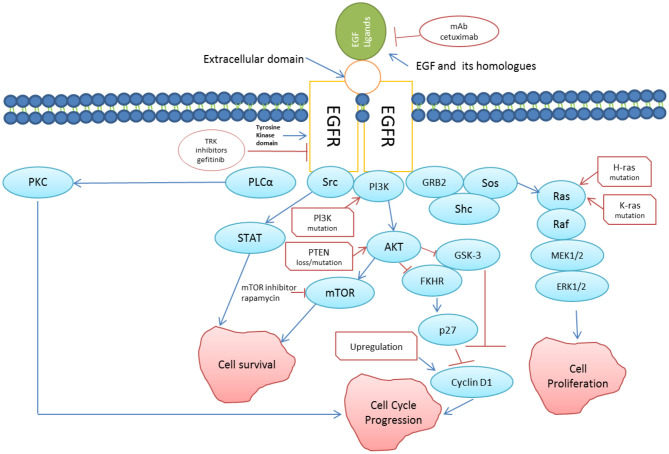
Figure 3.
EGFR signaling pathway (redrawn from [75]). Binding of EGF (and its homologs) to EFGR triggers directly or indirectly cascades of reactions leading to cell survival and cell proliferation. Somatic mutations in EGFR leading to persistent activation is linked to increased growth, reduced apoptosis, increased angiogenesis and metastasis, which are the key features of cancer progression. Two approaches using mAb against EGFR such as cetuximab, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors to suppress anomalous EGFR activation in cancer cells has been shown in the figure.