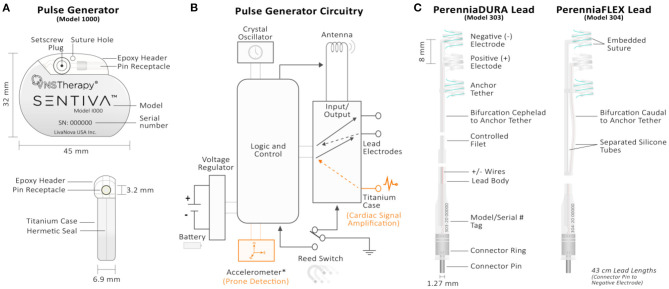
Figure 2.
Technical overview of the VNS Therapy System's implantable components. (A) Front (top) and side (bottom) views of the M1000 implantable pulse generator. The generator circuitry is hermetically sealed in a titanium case. A hex screwdriver is inserted into the setscrew plug receptacle during surgery to secure the lead's connector pin upon insertion. Model and serial number information are printed on the front face of each generator. (B) Pulse generator circuitry schematic. The generator's circuitry includes, (1) crystal oscillator to provide a timing reference; (2) voltage regulator to regulate the system power supply from the battery; (3) antenna to receive programming signals and transmmit telemetry information to the Programming Wand; (4) logic and control that receives and implements programming commands, as well as collects and stores telemetry information (i.e., memory); (5) input/output controller to develop and modulate signals delivered to the lead. It can also allow the traditional VNS to serve as both therapy outputs and sensing inputs; (6) reed switch controlled by swiping the therapy's patient magent. For the M106, M1000, and M1000-D generators, the logic and control also processes sensory information (heart rate) and controls sensory-based therapy outputs (AutoStim). Components unique to the therapy's closed-loop generators (models 106, 1000, and 1000-D) are shown in orange. The input controller of closed-loop generators through the titanium case connection provides cardiac signal amplification. The accelerometer is unique to M1000 and M1000-D generators and provides information related to patient posture for prone event detection. (C) Single-pin PerenniaDURA M303 (left) and PerenniaFLEX M304 (right) implantable leads. Each lead features two active helical electrodes (negative and positive) that provides therapy output and a non-active anchor tether electrode used for stabalization purposes. Embedded sutures in the silicone casing of the helical eletrodes allows manipulation with forceps during surgery. The increased flexibility of the M304 lead is provided by the separated silicone tube configuration (right).