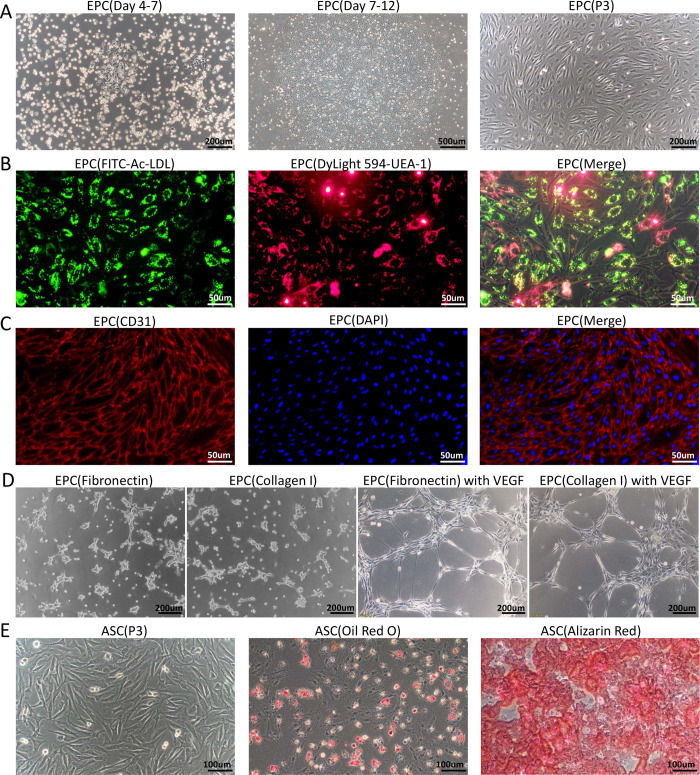
Fig 1. Isolation and characterization of rabbit EPCs and ASCs.
(A)Rabbit peripheral blood mononuclear cells were seeded on plates pretreated with fibronectin and supplemented with EGM-2 complete medium. At 4 to 7 days, adherent cells with typical cobblestone-like morphology appeared. At 9–12 days, the EPCs expanded into colonies. Third-passage EPCs cultured in complete EGM-2 medium exhibited spindle-like morphology under inverted phase-contrast microscopy. (B) The functional characteristics of EPCs were assessed by testing their ability to take up FITC-Ac-LDL and bind to DyLight 594-UEA-1. The results were visualized with fluorescence microscopy. (C) Immunofluorescent staining revealed the expression of endothelial cell marker CD31 in EPCs. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI. (D) Representative mages of the tube formations of EPCs isolated by fibronectin or collagen I coating methods, the EPCs were resuspended with EGM2 basal medium containing 50ng/ml VEGF or not, respectively. (F) Third-passage ASCs cultured in complete EGM-2 medium displayed fibroblast-like morphology. The multilineage differentiation potential of ASCs was assessed in vitro. Osteogenesis was assessed by staining with Alizarin Red to detect the formation of calcium-rich deposits. Adipogenesis was assessed by staining with Oil red O to detect lipid vacuoles in the cytoplasm.