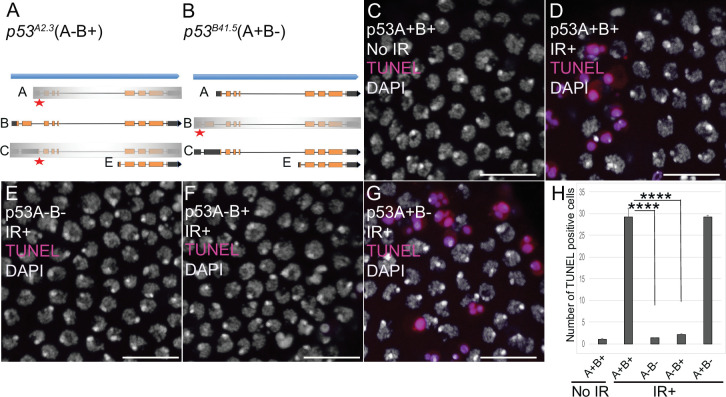
Figure 2. p53A is necessary and sufficient for IR-induced apoptosis in the soma.
(A–B) The p53 isoform-specific mutants created at the endogenous p53 locus with CRISPR / Cas9. Each allele is a small deletion (red asterisk) in the unique 5’ coding exon of p53A (A) and p53B (B) mRNAs. The p53A2.3 (A-B+) mutant impairs expression of isoforms p53A and p53C (gray shading) but not p53B, whereas the p53B41.5 (A+B-) mutant eliminates expression of p53B (gray shading) but not p53A (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1). (C–H) Apoptotic response to IR of stage six somatic follicle cells, assayed by TUNEL (red), with DNA stained with DAPI (gray). (C–D) TUNEL-labeled follicle cells from a p53+ (A+B+) wild type female without (C) or 4 hr after IR (D). (E–G) TUNEL labeling of follicle cells after IR from p535A-1-4 (A-B-) null (E), p53A2.3 (A-B+) (F), and p53B41.5 (A+B-) (G) mutant females. Scale bars are 10 μm. (H) Quantification of the average number of TUNEL-labeled follicle cells in stage six egg chambers for the genotypes and treatments shown in (C–G). Averages are based on 10 egg chambers per genotype with two biological replicates. Error bars are S.E.M. ****: p < 0.0001 by unpaired Student’s t test.