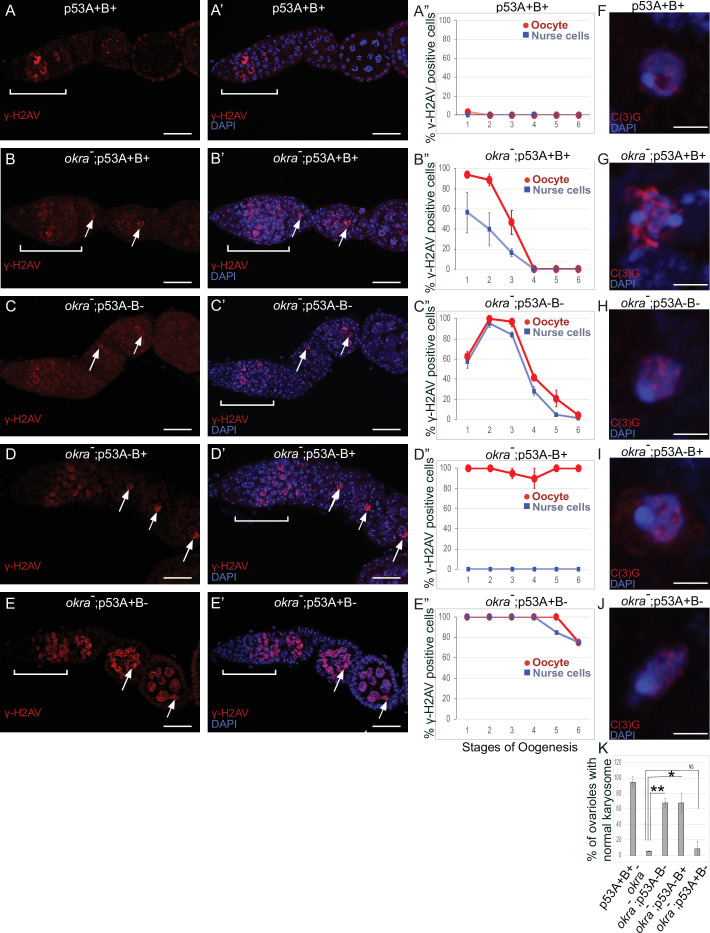
Figure 7. p53A and p53B have overlapping and distinct functions in germline genome integrity and the meiotic pachytene checkpoint.
(A-E’) Drosophila ovarioles of indicated genotypes were immunolabeled for γ-H2Av (red A-E) to detect DNA breaks and counterstained with the DNA dye DAPI (blue A’-E’). The ovarioles are shown with the anterior germarium to left (square bracket). Scale bars are 25 µm. (A”-E”) Quantification of percent of ovarioles with γ-H2Av-positive nurse cells (blue squares) and oocyte (red ovals) at different stages. Values are means of five biological replicates and >20 ovarioles with error bars representing S.E.M. Those values that had low variance have very small error bars that are not visible in the graphs. See Figure 6—figure supplement 1 for higher mag images of germaria, and Supplementary file 1 for p values. (F–K) p53A is required for activation of the pachytene checkpoint. (F–J) Oocyte nuclei from stage 3 to 4 egg chambers labeled with antibodies against synaptonemal protein C(3)G (red) and DNA dye DAPI (blue). (F) Wild type with spherical compact karyosome. (G) okraRU / okraAA with diffuse chromatin indicating activation of the pachytene checkpoint. (H) okraRU / okraAA; p535A-1-4 (A-B-) null with compact spherical karyosome. (I) okraRU / okraAA; p53A2.3 (A-B+) p53A mutant with spherical karyosome. (J) okraRU / okraAA; p53B41.5 (A+B-) with elliptical nucleus. Scale bars are 3 µm. (K) Quantification of karyosome formation. Data are means based on two biological replicates with ~30 nuclei per strain per replicate, with error bars representing S.E.M. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, n.s. = not significant by unpaired Student’s t test.
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Images of eggshell phenotype classes produced by p53 and okr single or double mutant mothers.
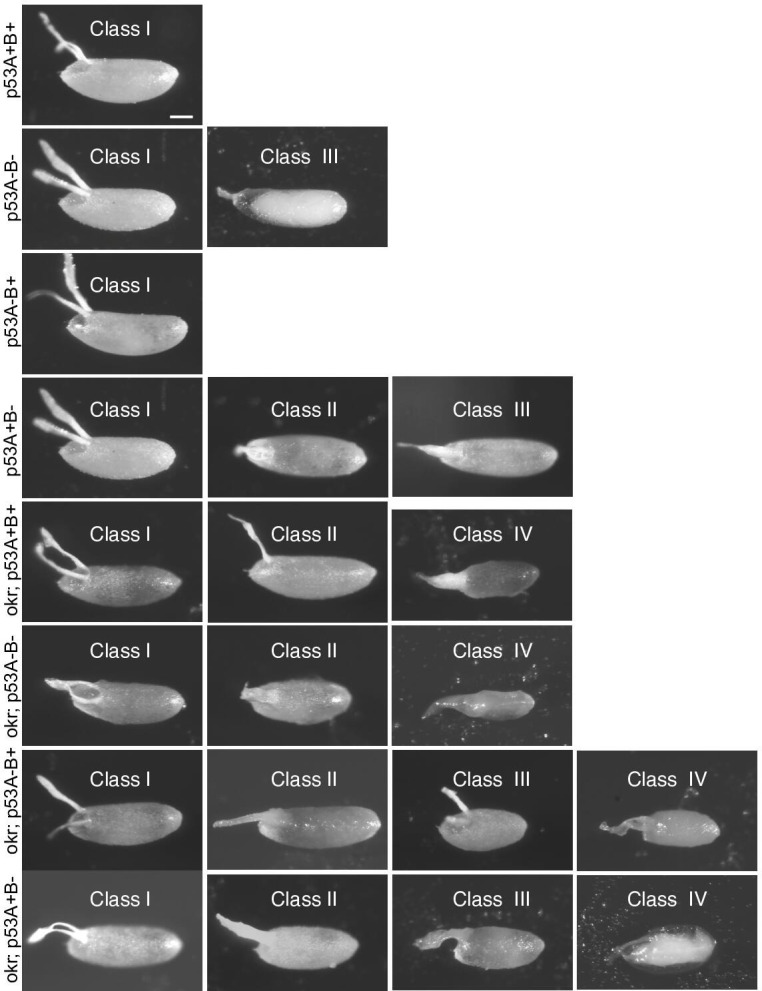
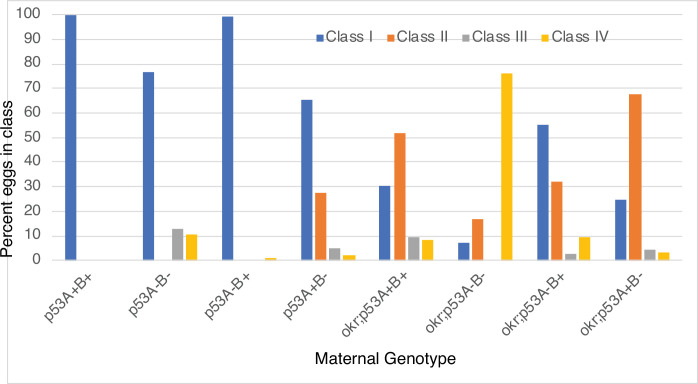
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Quantification of eggshell phenotype classes produced by p53 and okr single or double mutant mothers.
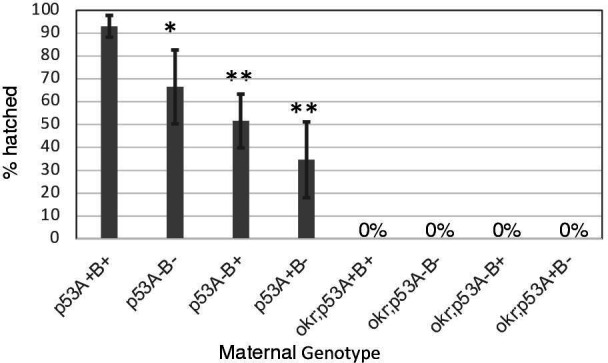
Figure 7—figure supplement 3. p53 mutant mothers have reduced fertility.