Fig. 4. Glycolytic SCs are metabolically coupled to injured axons and antagonize AxD.
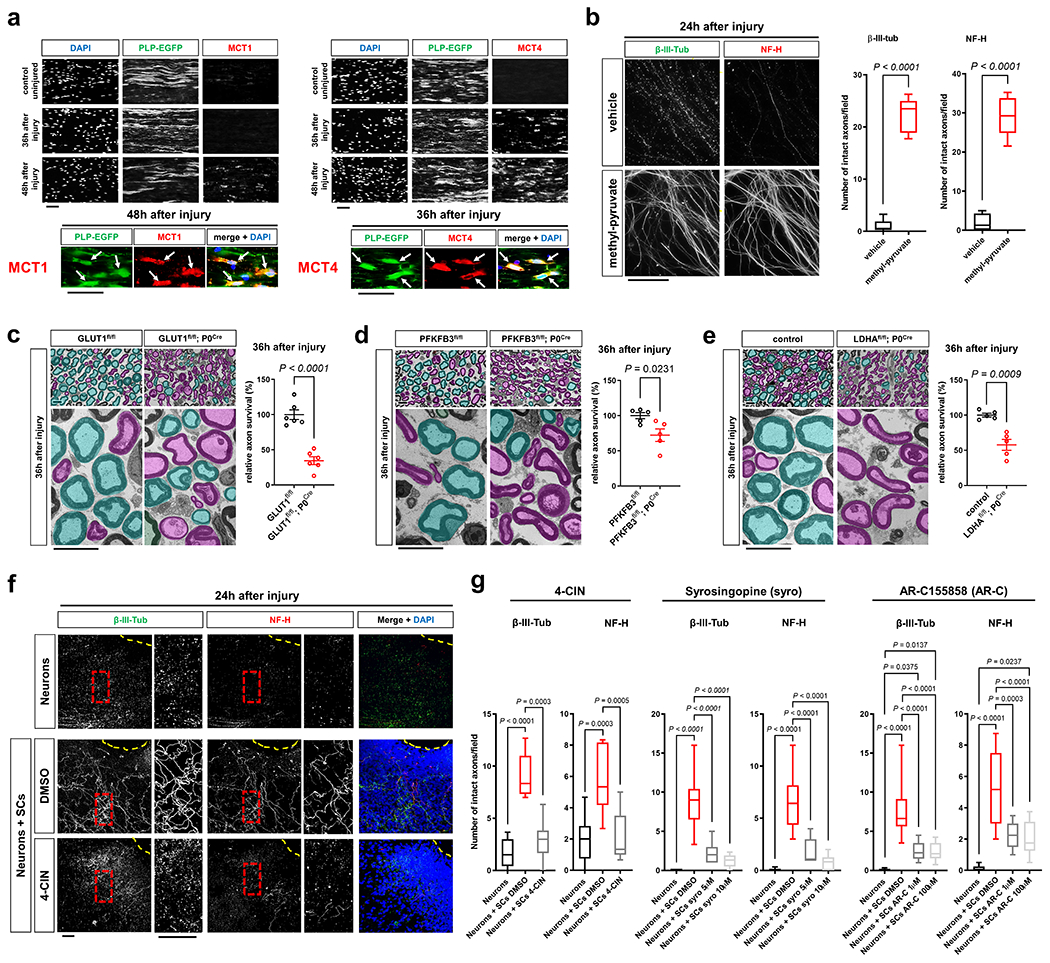
a, Representative immunofluorescence for the indicated MCTs on longitudinal frozen sections from control uninjured nerves and axotomized distal sciatic nerve stumps at the shown post-injury time points. Arrows depict colocalization. Scale bars: 50μm. The experiment was reproduced three times independently with similar results. b, Left: Representative micrographs show immunolabeled axons 24h after disconnection from the neuronal cell bodies under the indicated conditions. Scale bar: 100μm. Right: Box and whiskers plots (maximum, 25th percentile, median, 75th percentile, minimum) of axon survival 24h following injury (n=36 DRG neurite preparations for both β-III-tub and NF-H per condition from 4 experimental sets performed on different days). c-e, Representative semithin (top) and electron micrographs (bottom) of transverse sciatic nerve sections of distal nerve stumps from mice with the indicated genotypes 36h after sciatic nerve transection with pseudocoloring of intact (turquoise) and degenerated (magenta) myelinated fibers, and corresponding quantifications of relative axon survival (Error bars represent s.e.m. n=6 mice per genotype for c. n=5 mice per genotype for d and e). Scale bars: 10μm. f, Representative immunofluorescence of axons 24h after disconnection from the neuronal cell bodies under the indicated conditions. Yellow dotted lines indicate axotomy sites. Insets show red dashed areas (red). Note many continuous transected axons in the preparation associated with SCs (middle panel), and abrogation of such axon protection in presence of 4-CIN (bottom panel). Scale bars: 50μm. The experiment was reproduced three times independently with similar results. g, Box and whiskers plots (maximum, 25th percentile, median, 75th percentile, minimum) of axon survival 24h following axotomy under the indicated conditions (4-CIN: β-III-tub and NF-H, Neurons: n=24 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs DMSO: n=25 DRG neurite preparations for β-III-tub and n=24 for NF-H, Neurons+SCs 4-CIN: n=21 DRG neurite preparations; all DRG neurite preparations from three experimental sets performed on different days. Syrosingopine: β-III-tub, Neurons: n=34 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs DMSO: n=37 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs syro 5μM: n=11 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs syro 10μM: n=30 DRG neurite preparations; all DRG neurite preparations from three experimental sets performed on different days except Neurons+SCs syro 5μM (one experimental set), NF-H, Neurons: n=34 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs DMSO: n=29 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs syro 5μM: n=11 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs syro 10μM: n=30 DRG neurite preparations; all DRG neurite preparations from three experimental sets performed on different days except Neurons+SCs syro 5μM (one experimental set). AR-C155858: β-III-tub, Neurons: n=41 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs DMSO: n=49 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs AR-C 1μM: n=24 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs AR-C 100μM: n=44 DRG neurite preparations; all DRG neurite preparations from three experimental sets performed on different days except Neurons+SCs AR-C 1μM (two experimental sets), NF-H: Neurons: n=41 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs DMSO: n=41 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs AR-C 1μM: n=24 DRG neurite preparations, Neurons+SCs AR-C 100μM: n=44 DRG neurite preparations; all DRG neurite preparations from three experimental sets performed on different days except Neurons+SCs AR-C 1μM (two experimental sets).
Statistical evaluation in b-e was performed using Student’s t-test, unpaired, two-tailed, and in g using One-way-ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons tests.
