Figure 1:
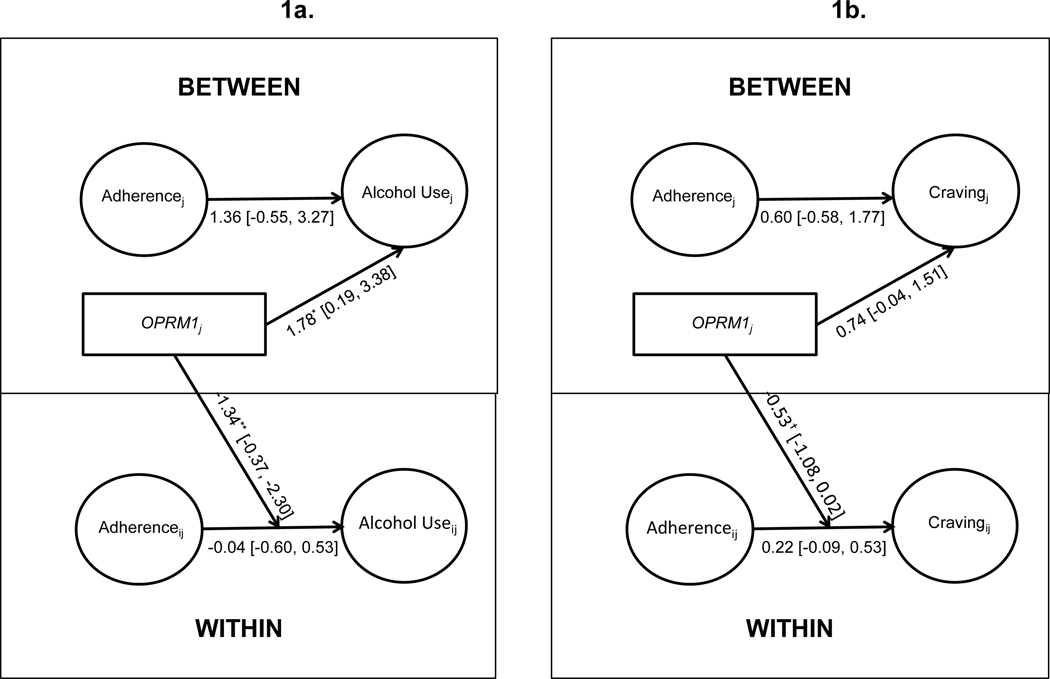
Multilevel structural equation models (MSEM) evaluating between- and within-person associations of daily naltrexone adherence with same-day alcohol use (1a) and craving (1b) and moderation by OPRM1 genotype. The moderation effect represents the regression of variance in the random slopes for within-person associations (i.e., adherence to drinking/craving) on OPRM1. Unstandardized parameter estimates shown. The associations of OPRM1 with the intercept represent OPRM1 differences in mean drinking levels, adjusted for intervention condition, race, and overall adherence. The OPRM1 moderation of within-person daily-level association between taking naltrexone and same-day values of the outcome adjusted for intervention condition and race. This figure depicts a simplified version of the model in which the random slopes are omitted. OPRM1 was coded GA/GG = 1, AA = 0.
†p<.10; *p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001.
