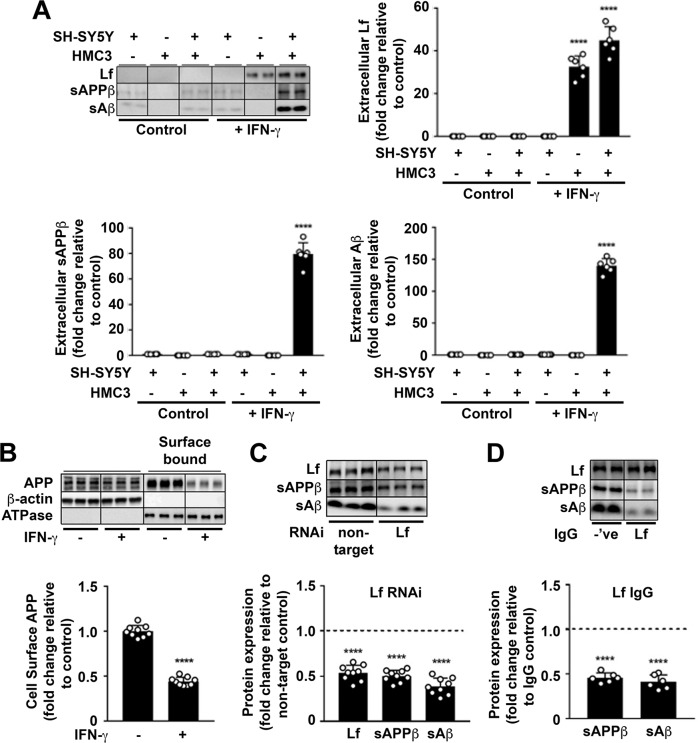
Fig. 6. Secreted holo-Lf from activated microglia reduces neuronal surface-presented APP and increases APP amyloidogenic processing.
A In monocultures and a transwell co-culture with HMC3 microglia cultured in the upper inserts and wt-APP695 SH-SY5Ys in the lower wells, human recombinant IFN-γ (10 ng/ml; 24 h) was used to activate microglia, as confirmed by the MHC class II marker (Supplementary Fig. S9A). IFN-γ-induced changes in media levels of secreted Lf, sAPPβ and Aβ were quantified from western blotting. B From transwell co-culture as in (A), surface APP from wt-APP695 SH-SY5Y co-cultures were measured by surface biotinylation after microglial activation. C HMC3 cells transfected with control non-target or Lf RNAi (20 nM; 48 h) were added to transwell co-cultures with wt-APP695 SH-SY5Y and activated with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml; 24 h) to determine expression levels of sAPPβ and Aβ secretion from wt-APP695 SH-SY5Y. D In a neutralising antibody inhibition assay, a polyclonal for Lf or an isotypic control IgG (20 μg/ml) was added to the media of wt-APP695 SH-SY5Y in the transwell co-culture before microglial activation by IFN-γ (10 ng/ml; 24 h). Inhibition of Lf binding to APP by the antibody was determined by measuring secreted Lf and the APP amyloidogenic protein fragments (sAPPβ and Aβ) in neuronal media. Data are mean ± SEM of three experiments performed in duplicate as a minimum and normalised against a control protein. Statistical analysis was by two-tailed t-tests compared to corresponding cell line without IFN-γ (A, B), non-target control (C) or isotype IgG treatment (D), ****p < 0.0001.