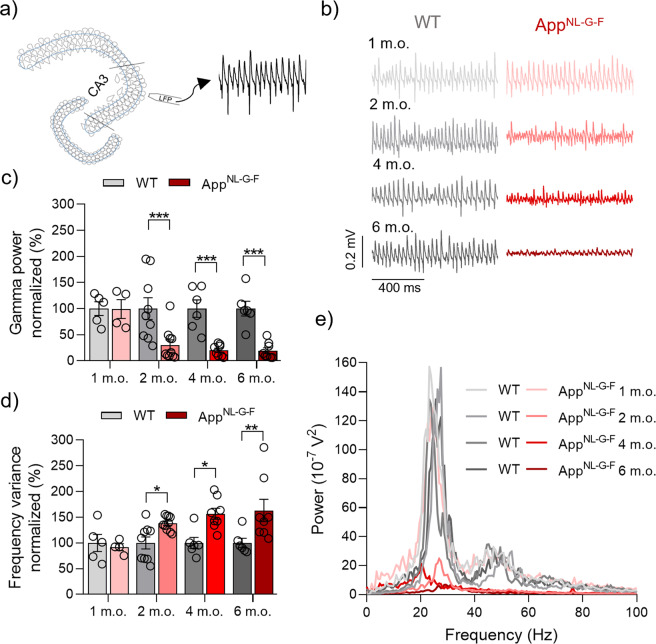
Fig. 1. Early degradation of KA-induced gamma oscillations in AppNL-G-F mice.
a Representative diagram of LFP electrode location in CA3 region of hippocampal acute slices. b Representative sample traces of LFP recordings from WT (left side) and AppNL-G-F (right side) at 1 m.o., 2 m.o., 4 m.o. and 6 m.o. c Summary of normalized gamma oscillation power at 1 m.o. (WT N = 5 vs AppNL-G-F N = 4, p = 0.9724), 2 m.o. (WT N = 9 vs AppNL-G-F N = 10, p = 0.0006), 4 m.o. (WT N = 6 vs AppNL-G-F N = 8, p = 0.0006) and 6 m.o. (WT N = 6 vs AppNL-G-F N = 8, p = 0.0006) for WT (gray bars) and AppNL-G-F (red bars) showing a strong degradation in AppNL-G-F mice from 2 m.o. onwards. d Summary of normalized frequency variance at 1 m.o. (p = 0.7254), 2 m.o. (p = 0.036), 4 m.o. (p = 0.0102) and 6 m.o. (p = 0.0051) for WT (gray bars) and AppNL-G-F (red bars) showing loss of regularity of gamma oscillations in AppNL-G-F from 2 m.o. onwards. e Representative power spectra from WT (gray lines) and AppNL-G-F (red lines), at the different ages analyzed. Data in bar graphs are presented as mean ± SEM. “N” indicates the number of mice. Statistics from two-way ANOVA followed by a Holm–Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (Supplementary Table 1). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.