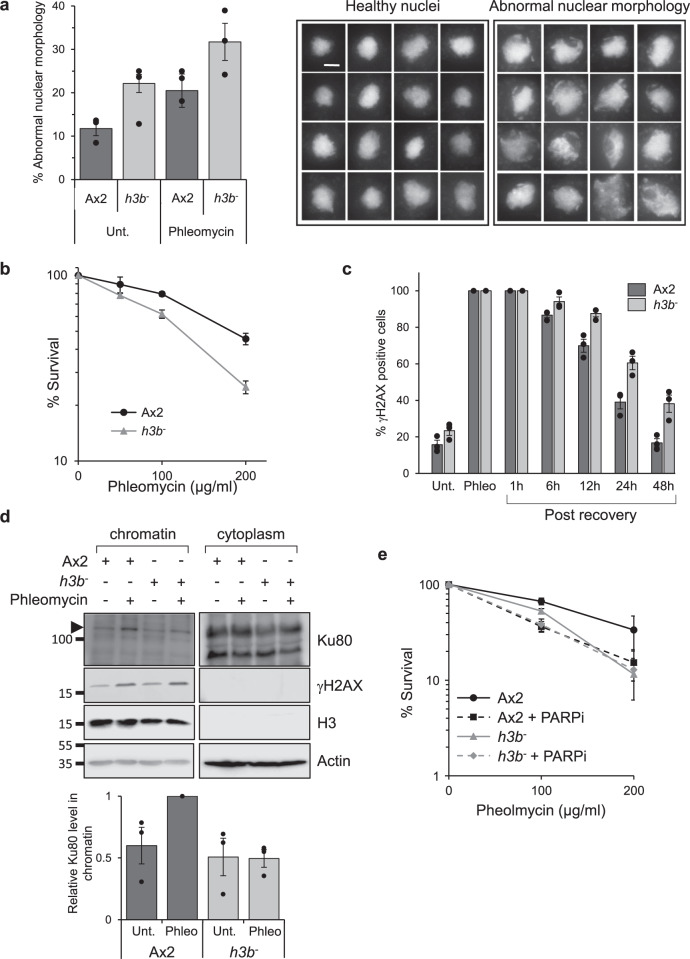
Fig. 1. H3b is required for DSB repair and genome stability.
a Abnormal nuclear morphology in the h3b− strain. Left panel: Quantification of cells displaying abnormal nuclear morphology in Ax2 or h3b− cells either in control conditions or 48 h after a 1 h exposure to phleomycin (n = 3; individual data points are shown, error bars represent the SEM). Right panel: representative pictures of healthy and abnormal nuclei. DNA is stained with DAPI and each nucleus has a diameter of 14.5 μm. Scale bar represents 5 μm. b Ax2 or h3b− cells were exposed to phleomycin for 1 h at the indicated concentrations and cell survival assessed by clonogenic survival assays (data represent three biological repeats, error bars represent the SEM). c Ax2 or h3b− cells were treated for 1 h with phleomycin and following recovery in fresh media, cells with >5 γH2AX foci assessed by immunofluorescence. (data represent three biological repeats; individual data points are shown, error bars represent the SEM). d Following exposure of Ax2 or h3b− cells to phleomycin for 1 h, cytoplasmic and chromatin fractions were prepared from cells and western blotting performed using the indicated antibodies (left panel). Enrichment of Ku80 in chromatin fractions was quantified from three independent experiments (right panel). Molecular weight markers are indicated in kDa. e Ax2 or h3b− cells were exposed to phleomycin for 1 h at the indicated concentrations either the absence or presence of olaparib (PARPi) and cell survival assessed by clonogenic survival assays (data represent four biological repeats; error bars represent the SEM). Source data are provided in the Source Data file.