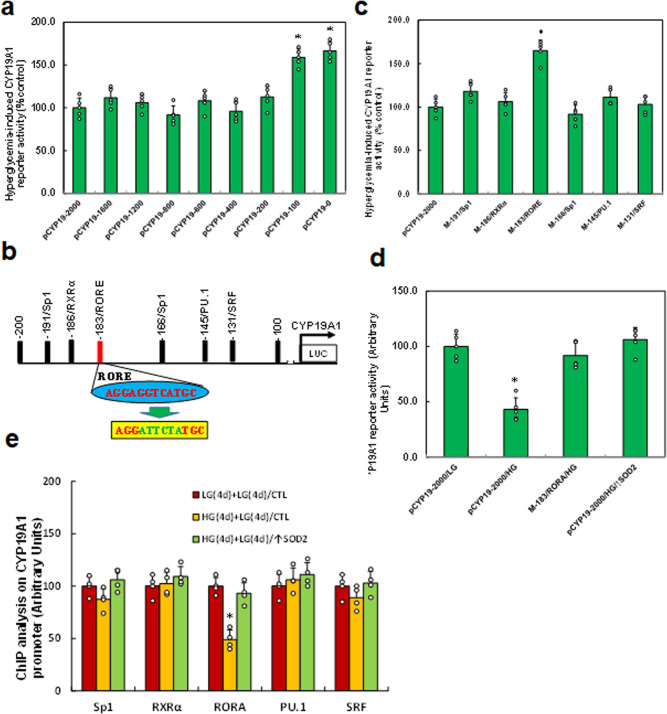
Fig. 3. Hyperglycemia induces CYP19A1 suppression through RORA dissociation from the RORE response element on the CYP19A1 promoter.
a The conditional immortalized ACS-5003 neurons were transiently transfected with either CYP19A1 full length (pCYP19-2000) or deletion reporter plasmids. After 24 h, the cells were treated with either 5 mM low glucose (LG) or 25 mM high glucose (HG) for 3 days and the relative CYP19A1 reporter activities were calculated n = 5. *, P < 0.0001, vs. pCYP19-2000 group. b The schematic picture for the potential transcriptional binding motif in the range of −200 to 100 (from transcription start site) on the CYP19 promoter with one potential RORA response element (RORE) marked in red as well as related mutation site marked in green. c The cells were transiently transfected by either a wild-type CYP19 reporter construct (pCYP19-2000) or single point mutation at the site shown in (b), and then treated with either LG or HG for 3 days, and the CYP19A1 reporter activities were calculated n = 5. *, P < 0.0001, vs. pCYP19-2000 group. d The cells were transiently transfected by CYP19A1 full length (pCYP19-2000), single mutant, or infected by SOD2 lentivirus (↑SOD2), and then treated with either LG or HG for 3 days; the CYP19A1 reporter activities were then calculated, n = 5. *, P < 0.0001, vs. pCYP19A1-2000/LG group. e Cells were treated with either 4-day LG plus 4-day LG (LG(4d)+LG(4d)), or 4-day HG plus 4-day LG (HG(4d)+LG(4d)), or infected on day 4 by SOD2 lentivirus (HG(4d)+LG(4d)/↑SOD2); the cells were then used for ChIP analysis by potential transcription factors on the CYP19A1 promoter, n = 4. *, P < 0.0001, vs. LG(4d)+LG(4d)/CTL group. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM.