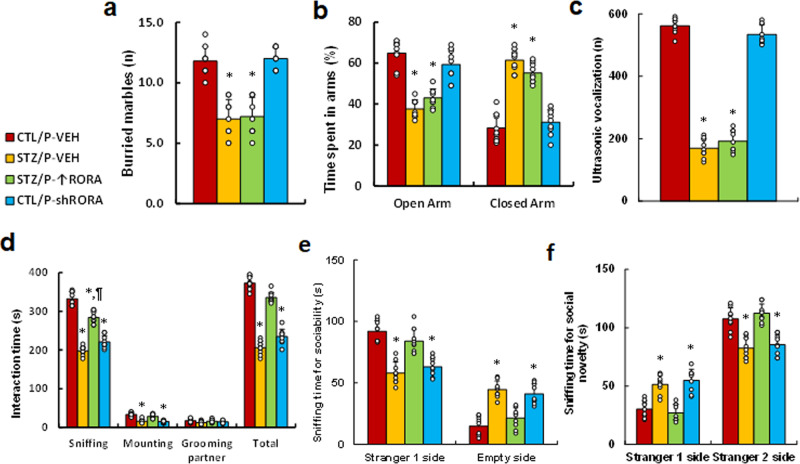
Fig. 7. Postnatal manipulation of RORA in the amygdala partly modulates maternal diabetes-induced autism-like behavior but has little effect on maternal diabetes-induced anxiety-like behavior in offspring.
Male offspring from either the control (CTL) or maternal diabetes (STZ) groups received either vehicle (P-VEH) or lentivirus infusion for either RORA expression (P- ↑ RORA) or RORA knockdown (P-shRORA) at 6 weeks old, and the male offspring were used for animal behavior analysis. a Marble-burying test (MBT), n = 9. b Time spent in the Open Arm and Closed Arm in the EPM test, n = 9. c Ultrasonic vocalization, n = 9. d Social interaction (SI) test, the time spent following, mounting, grooming, and sniffing any body parts of the other mouse was calculated, n = 9. e, f Three-chambered social tests, n = 9. e Time spent in the chamber for sociability. f Time spent in the chamber for social novelty. *, P < 0.0001, vs. CTL/P-VEH group; ¶, P = 0.0001, vs. STZ/P-VEH group. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM.