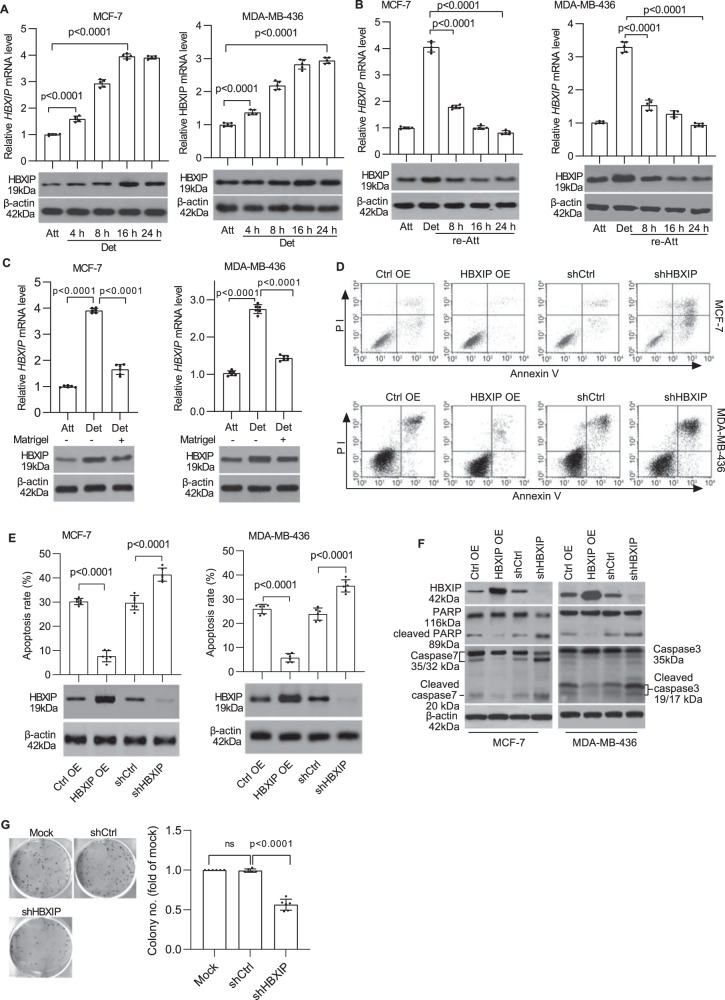
Fig. 1. HBXIP is upregulated following ECM detachment and induces anoikis resistance in breast cancer cells.
A MCF-7 and MDA-MB-436 cells were detached and cultured in suspension in poly-HEMA-coated plates for the indicated times. HBXIP mRNA and protein levels were measured using qRT-PCR (upper panel) and western blot analysis (lower panel), respectively. B MCF-7 and MDA-MB-436 cells cultured in suspension for 8 h were reattached for the indicated times and subsequently subjected to qRT-PCR and immunoblot analysis to determine the mRNA and protein levels of HBXIP. C qRT-PCR and immunoblot analysis of the HBXIP mRNA and protein expression levels in attached cells and detached cells cultured in complete medium with or without a Matrigel basement membrane-like matrix for 12 h. D The stable HBXIP overexpression and knockdown cells were cultured in suspension for 24 h and stained with Annexin V. The flow cytometry profile shows Annexin V-FITC staining on the x-axis and PI staining on the y-axis. FSC/SSC plot and gating strategies were shown in Supplementary Fig. 4. E Histograms indicating the percentages of apoptotic cells (early and late apoptosis) in D under the indicated conditions. Immunoblots showing HBXIP expression in the indicated stable cell lines. F Western blot analysis was performed to detect caspase-3 (or caspase-7), PARP, and cleaved caspase-3 (or cleaved caspase-7) and PARP levels in the stable cell lines described in D. G A soft agar colony formation experiment was performed to detect the anchorage-independent growth of HBXIP-deficient MDA-MB-436 cells. The error bars indicate the ±SD values as assessed by Student’s t test. All experiments were performed at least three times.