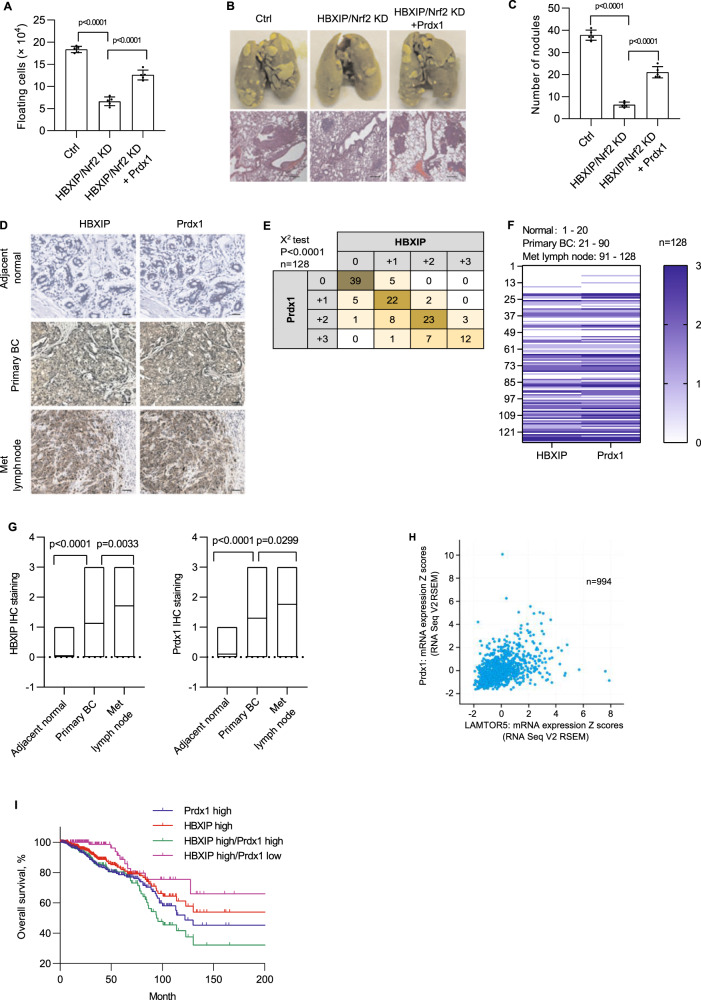
Fig. 6. The HBXIP/Nrf2 feedback loop induces metastasis and anoikis resistance in breast cancer cells in vivo.
A At 4 days after the i.p. injection with stable HBXIP/Nrf2 KD MDA-MB-436 cells and stable Prdx1 OE HBXIP/Nrf2-deficient MDA-MB-436 cells, the viable cells were counted using the trypan blue exclusion assay after removing possible contaminating mouse cells. B Representative images of lung tissue and tissue sections from the indicated groups of mice were obtained 3 weeks after the tail vein injection of the indicated stable breast cancer cells. Scale bars, 200 μm. C The lung metastatic nodules in the mouse lungs shown in B were counted. D The expression of the HBXIP and Prdx1 proteins in normal breast tissues, primary breast cancer tissues, and metastatic lymph node tissues were examined using IHC. Scale bars, 50 μm. E The association between HBXIP and Prdx1 expression levels in the abovementioned IHC assay was statistically analyzed by χ2 test. F Heatmap of HBXIP and Prdx1 expression in the tumor tissues from each patient referenced in D. G Correlations between HBXIP and Prdx1 expression in patients with breast cancer are referenced in panel F. H Expression levels of the HBXIP and Prdx1 mRNAs (z scores, RNA Seq V2 RSEM) were analyzed in 994 clinical breast cancer samples (Pearson’s correlation coefficient; r = 0.43, Spearman’s correlation coefficient = 0.47). I The patients with breast cancer referenced in H were filtered into four groups (Prdx1 high = 359, HBXIP high = 354, HBXIP high/Prdx1 high = 215, HBXIP high/Prdx1 low = 139) according to the HBXIP and Prdx1 expression levels and z scores. An overall survival curve was generated using the Kaplan–Meier method, and results were statistically compared using a log-rank test. p values were determined using Student’s t test for the data shown in (A, C, and G) and using a chi-square test for the data in E.