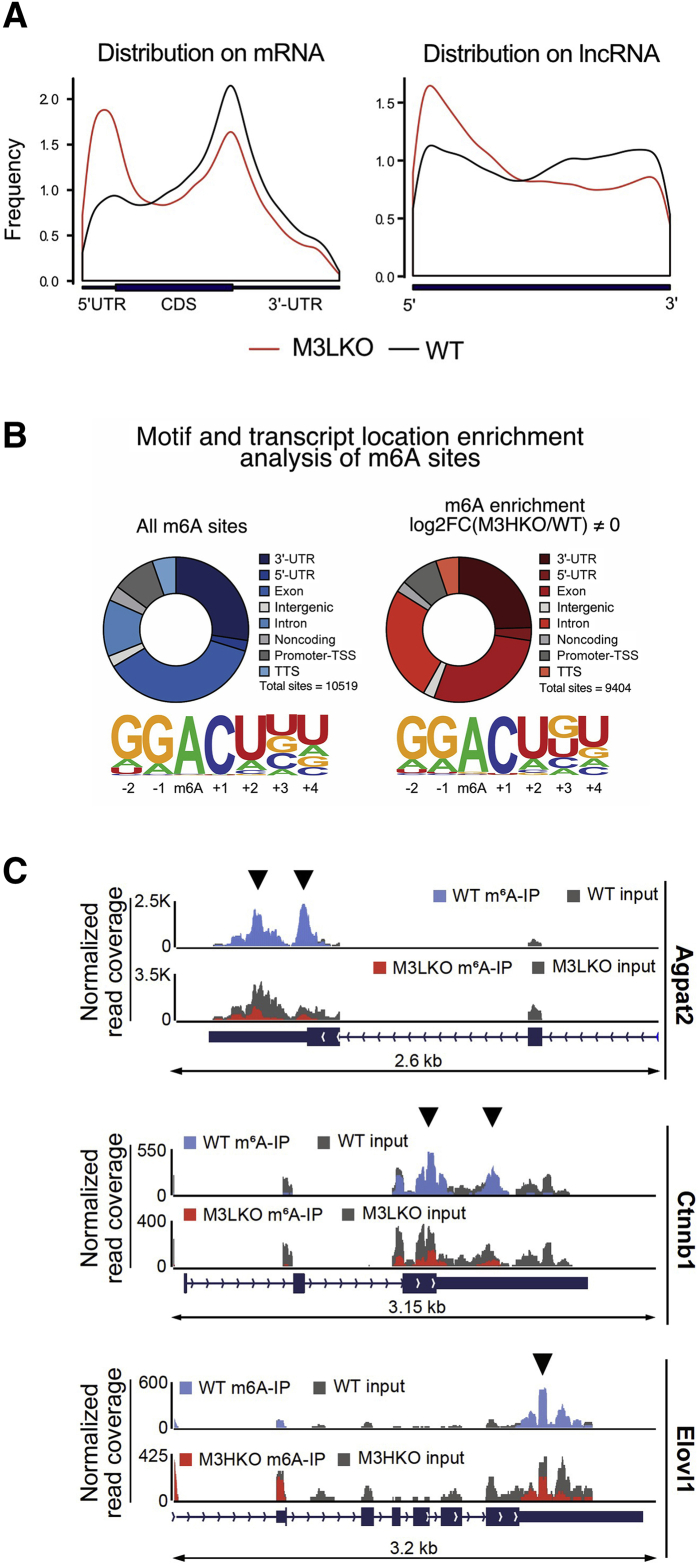
Figure 2.
Methylated (m6A) RNA immunoprecipitation (meRIP) coupled with sequencing analysis identifies polyadenylated RNAs with reduced m6A methylation at their 3′-UTRs and exons in liver-specific METTL3 knockout (M3LKO) livers compared with WT livers. A: Normalized distribution of high-confidence m6A sites on mRNAs and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in 5-week–old wild-type (WT) and M3LKO mice. Black lines indicate distribution of all m6A sites identified. Red lines denote distribution of all m6A sites found to have significantly altered enrichment in M3LKO livers (fold change in m6A enrichment (WT/M3LKO ≠ 0). Significant enrichment was calculated using ExomePeak finder with a rescaled hypergeometric test false discovery rate cut-off of P < 0.05 and absolute fold change enrichment >1. B: Motif enrichment for each peak type (all sites or altered sites) was identified by running Homer Motif Analysis. Only the most significant and prevalent motifs are shown. C: Peak distribution normalized to input in the genomic regions of 3 critical transcripts (Agpat2, Ctnnb1, and Elovl1) in the WT and M3LKO mice are shown. Sequencing tracks of these genes and enrichment in the m6A immunoprecipitation and input in the WT and M3LKO livers were visualized using Integrated Genome Viewer (IGV) software version 2.4.16 (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA). Arrowheads indicate m6A peaks. n = 4 per genotype (A). TSS, transcription start site; TTS, transcription termination site.