Fig. 1.
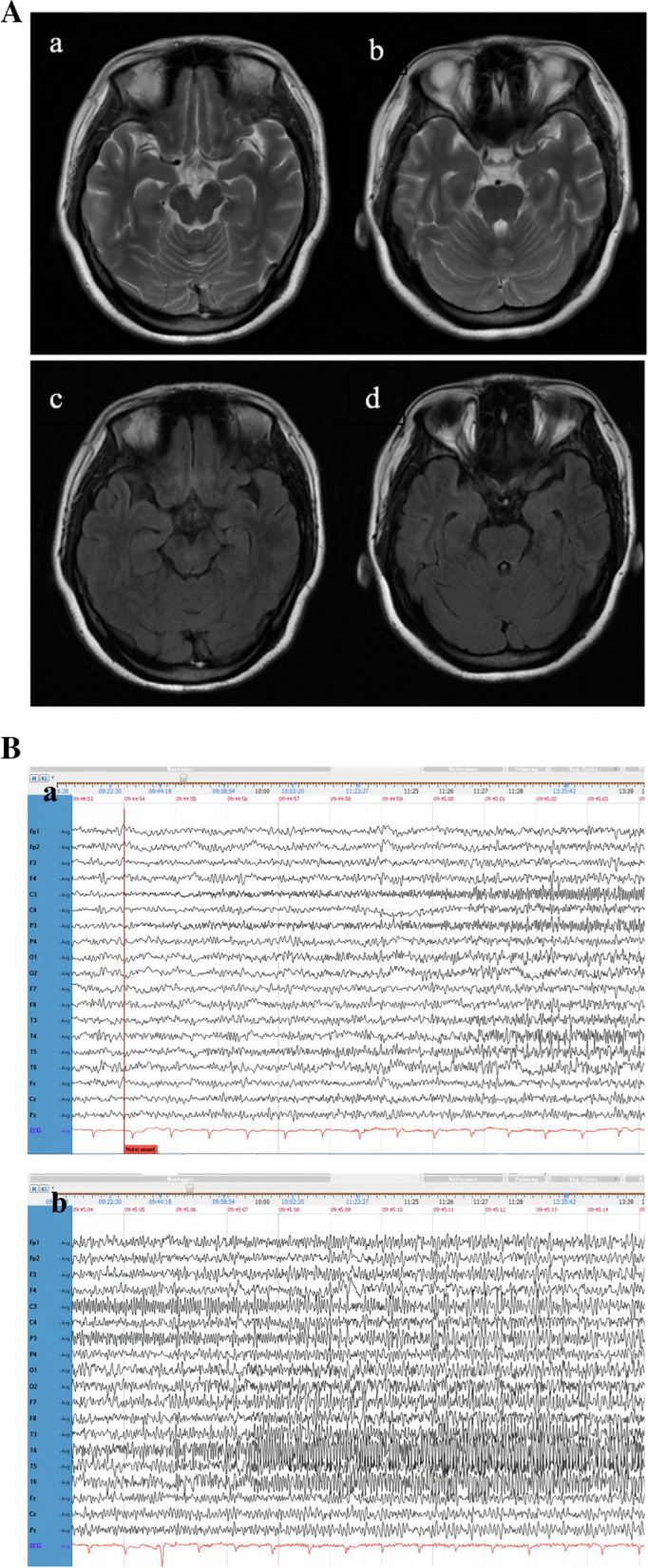
(A) Abnormal MRI signaling of one 28-year-old woman patient from the anti-NMDAR encephalitis with non-SE group. The brain MRI showed swelling and T2 FLAIR slightly hyperintensity in the bilateral temporal lobes. (a, b) T2-weighted MRI, (c, d) Axial T2 FLAIR sequences. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; FLAIR, fluid attenuated inversion recovery; non-SE, non-status epilepticus; anti-NMDAR, anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. (B) A representative EEG of the anti-NMDAR encephalitis patients with SE. High frequency beta activity in the left central and parietal lobe with progressively increasing amplitude, typical of the tonic phase in status epilepticus, was associated in this patient with dystonic posturing of his right arm (a and b are continuous records). anti-NMDAR, anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; SE, status epilepticus
