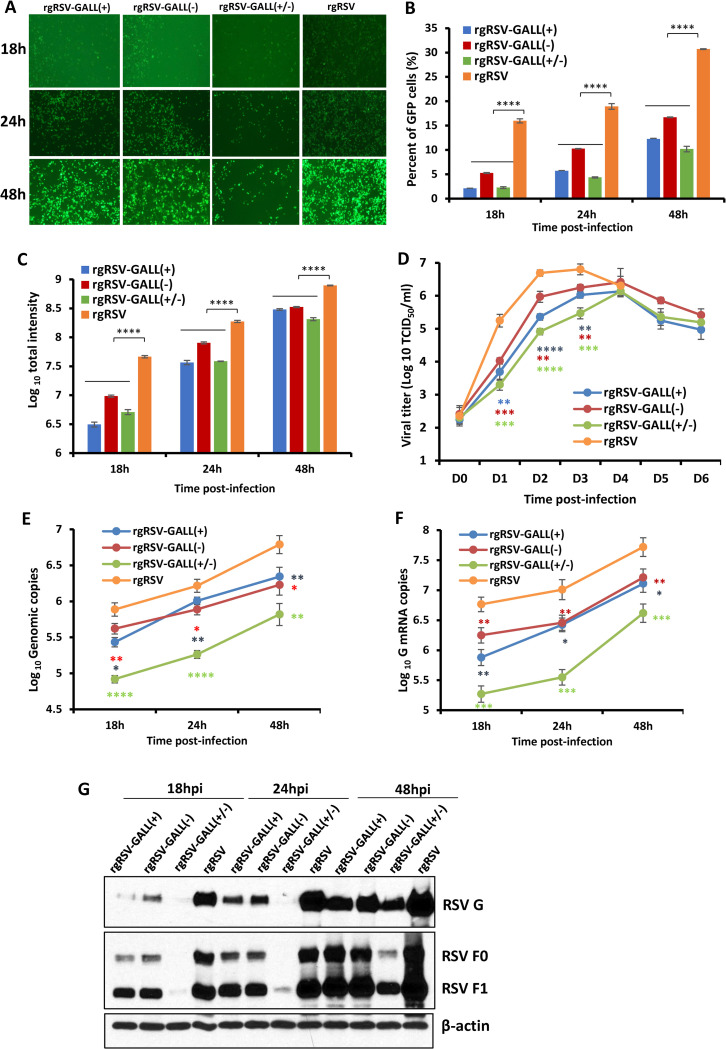
Fig 5. Replication of m6A-deficient RSVs is attenuated in A549 cells.
(A) Delayed GFP expression by rgRSV mutants in A549 cells. Confluent A549 cells were infected by each rgRSV at an MOI of 0.1, and GFP expression was monitored at the indicated times by fluorescence microscopy. (B-C) Quantification of GFP positive cells by flow cytometry. Confluent A549 cells were infected by each rgRSV (MOI of 0.1). At the indicated time points, cells were trypsinized and GFP positive cells (B) and GFP intensity (C) were quantified by flow cytometry. (D) Single-step growth curve of rgRSV mutants. A549 cells in 24-well-plates were infected with each recombinant rgRSV at an MOI of 0.1. The viral titer was determined by TCID50 assay in HEp-2 cells. (E) RSV genome RNA replication. At 18, 24, and 48 h post-infection, total RNA was purified from rgRSV-infected cells using TRizol, and genome RNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR using specific primers annealing to the RSV leader sequence and GFP gene. (F) RSV G mRNA transcription. Viral mRNA was quantified by real-time PCR using primers annealing to the G. (G) Western blot analysis of RSV F and G protein expression. A549 cells were infected with the parental rgRSV or rgRSV mutants at an MOI of 0.1. At 18, 24, and 48 h post-inoculation, total cell lysates were harvested and subjected to Western blotting using a monoclonal antibody against RSV F or G protein. The RNA copy and viral titers are the geometric mean titer (GMT) of three independent experiments ± standard deviation. Western blots shown are the representatives of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed using Student’s t-test and *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.