Figure 4. Loss of ATRX in murine neuronal precursor cells (mNPC) and murine GBM cells (mGBM) results in down-regulation of Chk1.
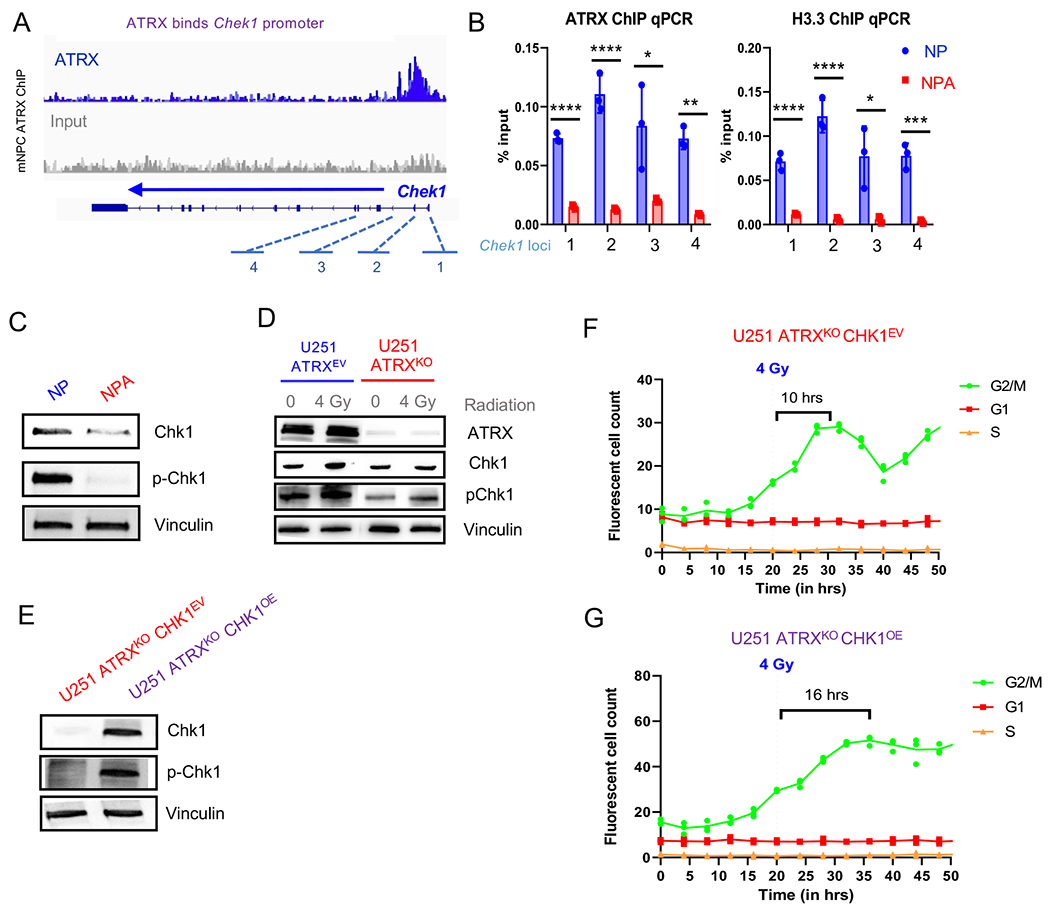
(A) ATRX promotor binding at Chek1 loci in mNPC cells (ChIP-seq, n=3 from Danussi et al., 2018). (B) mGBM cells with ATRXKO (“NPA”) show reduced ATRX and H3.3 binding at Chek1 gene loci (“1” through “4” from A) compared to mGBM cell controls without ATRXKO (“NP”), n=3. (C) Chek1 expression is downregulated in mNPC cells with ATRX loss. (D) Western blot of U251 ATRXEV and U251 ATRXKO cells with and without 4 Gy IR. ATR pathway proteins are marked in purple. (E) Western blot of U251 ATRXKO cells with isogenic Chk1 overexpression or empty vector (n=3 replicates for C and D). (F-G) Incucyte live cell imaging analysis of U251 ATRXKOChk1OE cells incorporated with the FastFUCCI reporter plasmid show a gradual return (more than 1.5X slower) to cycling after 4 Gy IR. (Mean ± SEM for triplicate experiments are shown. *P≤ 0.05, **P≤ 0.01, and ***P≤0.001 using Welch’s t-test). For additional data, see also Figure S4.
