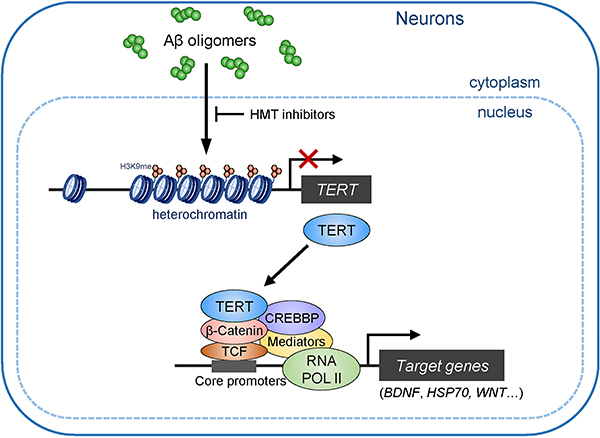
Extended Data Fig. 9: TERT contributes to β-Catenin/TCF-mediated transactivation in AD neurons.
At the early pathological stage of AD, amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers induce the transcriptional repression of TERT gene via the propagation of heterochromatin in neurons. Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of H3K9 methyltransferases (HMTs) can de-repress TERT gene suppression. TERT protein is able to interact with RNA pol II core transactivation machinery through β-Catenin and triggers the transcriptional induction of specific genes associated with neuronal survival and synaptic function in AD neurons, enabling to alleviate cognitive deficits.