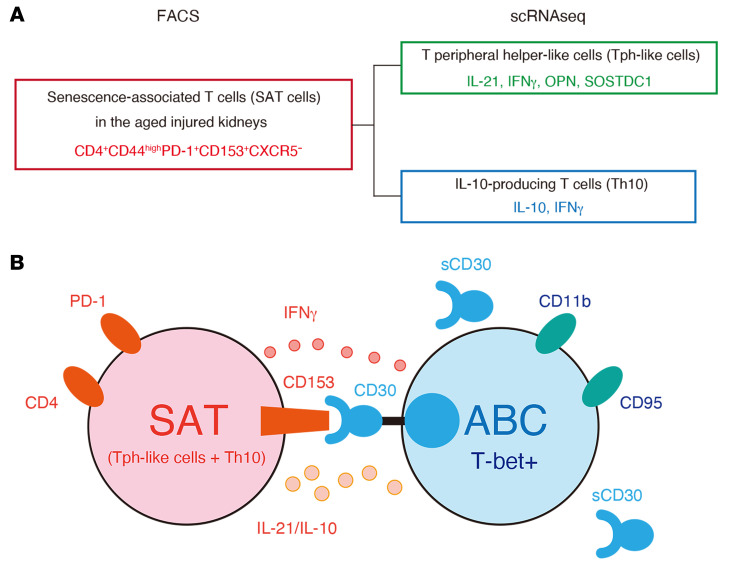
Figure 12. A model for interaction between SAT cells and ABCs within TLTs in aged injured kidneys.
(A) SAT cells in aged injured kidneys are defined as CD153+CD44hiPD1+CXCR5–CD4+ T cells by flow cytometry. SAT cells are classified into Tph-like cells and Th10 at transcriptional levels. (B) SAT cells express PD-1 and CD153 on their surface, whereas ABCs are positive for transcriptional factor T-bet, and express CD11b and CD95 on their surface. SAT cells produce IL-21, IL-10, and IFN-γ, all of which are essential for the induction of ABCs and germinal center B (GCB) cells and the acquisition of these B cell helper functions of SAT cells is dependent on CD153/CD30 signaling. In the absence of CD153/CD30 signaling, SAT cells lose their B cell helper function and are not fully capable of inducing ABCs and GCB cells, resulting in a reduction in number and size of TLTs. Cell-surface CD30 is quickly lost after activation by shedding and becomes the soluble form of CD30 (sCD30).