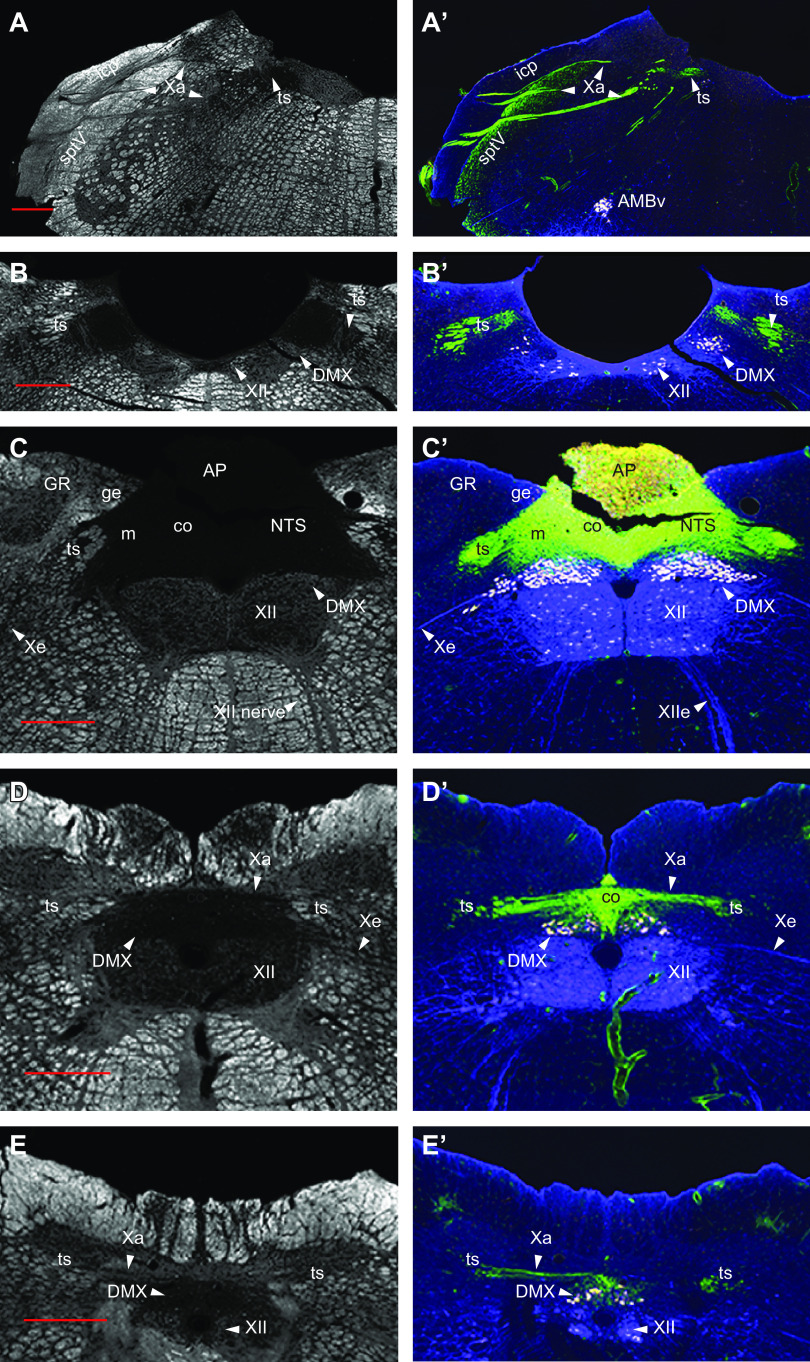
FIGURE 7.
Dark field (A–E) and fluorescent (A’–E’) photomicrographs of 5 rostral to caudal coronal sections of the medulla from a single male rat injected intraperitoneally with fluorogold to retrogradely label neurons that project outside the blood-brain barrier (white neurons in A’–E’). Isolectin B4 (IB4) binding was used to label primary sensory inputs, including those in the vagus nerve (green). Parasympathetic pre-ganglionic neurons are identified using choline acetyl transferase immunohistochemistry (blue), some of which also colocalize fluorogold. The photomicrographs show the distribution of vagal sensory nerves as they enter the dorsal medulla (A’), the solitary tract (A’ and B’), and then the entire rostrocaudal extent of the nucleus of the solitary tract (C’ and D’). Labeling in the area postrema is a mixture of fluorogold accumulated from the circulation and IB4. We thank Myrtha Arnold (ETH Zürich) for preparing the rat brain used in this figure. Red scale bars = 500 µm. AMBv, ambiguous nucleus, ventral division; AP, area postrema; DMX, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; GR, gracile nucleus; Icp, internal cerebellar peduncle; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; co, NTS, commissural part; ge, NTS, gelatinous part; m, NTS, medial part; sptV, spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve; ts, solitary tract; Xa, afferent nerve of the vagus; XII, hypoglossal nucleus; Xe, efferent nerve of the vagus; XIIe, efferent nerve of the hypoglossal.