FIGURE 18.
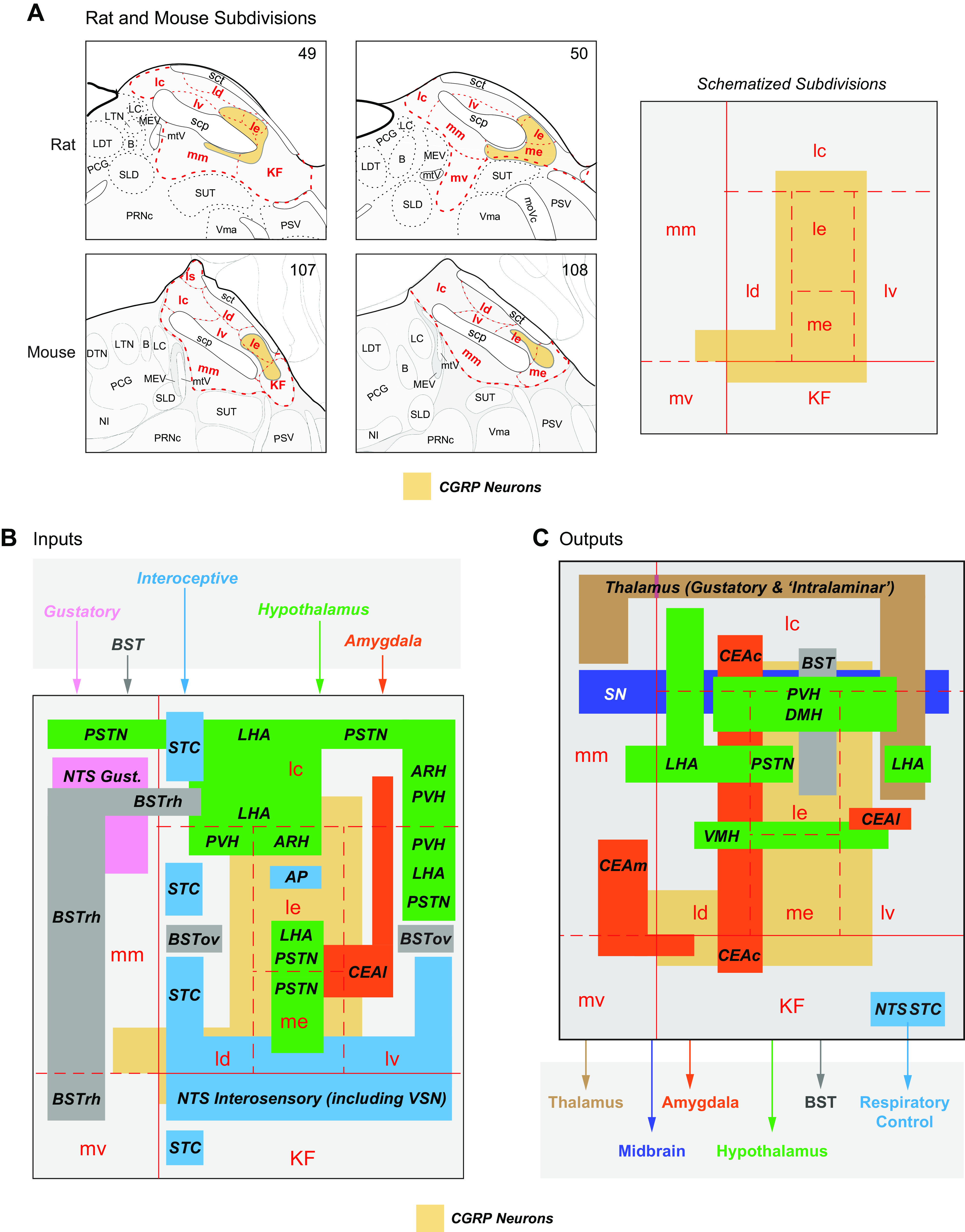
A: subdivisions of the parabrachial nucleus (PB) at levels 49 and 50 of Swanson Rat Brain Atlas (59) and levels 107 and 108 of the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas (66). The single panel on the right shows a schematized version of the rat and mouse PB showing the relative positions of the subdivisions based on the Atlas maps. Note that the size of the subdivisions is not to scale. The PB is part of a rhombicbrain network that makes significant contributions to eating behaviors control (see FIGURE 5). This control is mediated by its numerous wide-ranging connections. Their targets and origins in the various parts of the PB are summarized in B and C, respectively. Note that only those PB connections implicated in eating behavior control are shown in A and B. Source and target regions are color coded as follows: amygdala, orange; BST, bed nuclei of the terminal stria, gray; gustatory inputs, pink; hypothalamus, green; interoceptive inputs and autonomic outputs, blue; midbrain, dark blue; thalamus, brown. The regional locations of each set of connections derive from many papers that are cited in the text. calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) neurons are an important source of PB outputs, and their locations are shown in yellow in A–C. Their locations in the rat PB have been transcribed from Refs. 1117, 1143 and in the mouse PB from Refs. 767, 830, 1118. LTN, lateral tegmental nucleus; LC, locus ceruleus; KF, Kölliker-Fuse subnucleus; PSV, principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve; PRNc, pontine reticular nucleus, caudal part; MEV, midbrain nucleus of trigeminal nerve; PCG, pontine central gray; BST, bed nuclei of the terminal stria; PSTN, parasubthalamic nucleus; CEAm, central nucleus of the amygdala, middle part; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; lc, central part of the lateral division; ld, dorsal part of the lateral division; le, external part of the lateral division; lv, ventral part of the lateral division; KF, Kölliker-Fuse subnucleus; mm, medial part of the medial division; CEAL, central nucleus of the amygdala, lateral; SN, substantia nigra; STC, spinal trigeminal comple; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; ARH, arcuate nucleus; mm, medial part of the medial division; AP, area postrema; SUT, supratrigeminal nucleus; SLD, sublaterodorsal nucleus; scp, superior cerebellar penduncle; me, median eminence; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; PSV, principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve; Vma, motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve, magnocellular part; B, Barrington’s nucleus; mtV, midbrain tract of trigeminal nerve.
