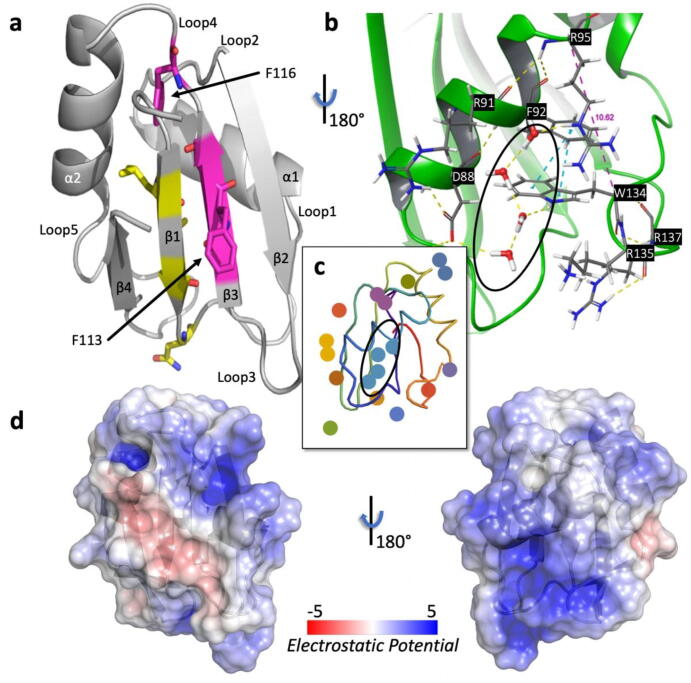
Fig. 1.
Structural features of TRMT2A RRM (resolution: 2.0 Å). (A), X-ray structure of the RRM in cartoon representation. The two central β-strands feature the submotifs RNP1 (β3 strand) and RNP2 (β1 strand). Canonical RNP1/2 residues found in TRMT2A RRM are highlighted (RNP2 as yellow sticks on the β1-strand and RNP1 as magenta sticks on the β3-strand). The sidechain of F113, part of RNP1, is solvent-exposed. In contrast, the sidechain of F116 (part of RNP1 as well) is buried and part of loop 4. (B), View of the lower helical site of the RRM and the water network. This view of the protein was obtained by rotating the protein’s orientation shown in A by 180°. The sidechain of W134 π-stacks with F92 (blue dashed lines). The Cα distance between R95 and W134 is highlighted as a purple dashed line (see subsequent sections). (C), Agglomerative Euclidean-distance-based clustering. Discs with the same color belong to the same water cluster. The largest cluster is circled as in B. (D), Electrostatic surface obtained with the Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver (APBS) [67] Electrostatics PyMOL plugin and mapped onto the solvent accessible surface in units of kT/e. The same protein’s orientations in A and B, respectively, were preserved. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)