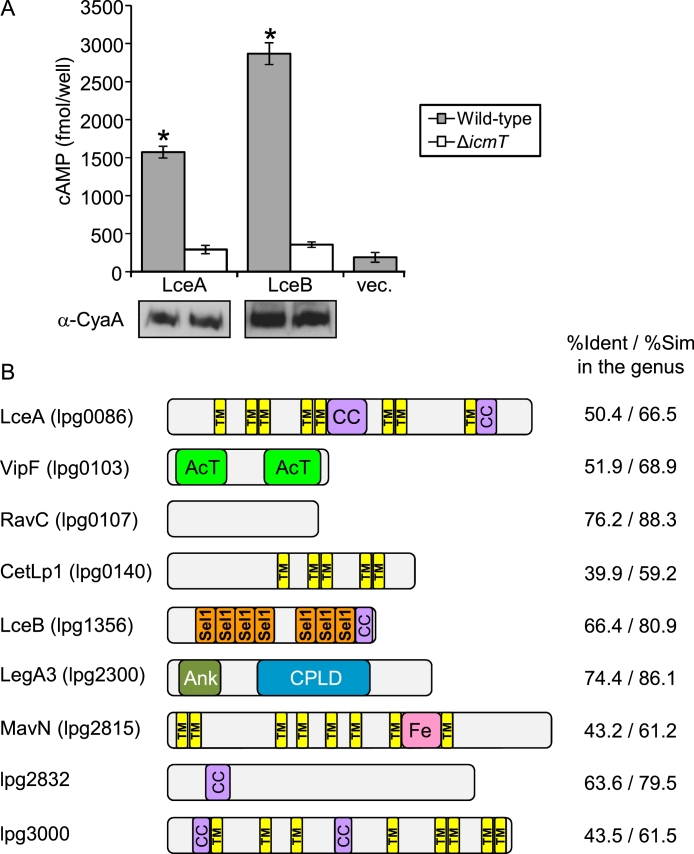
Fig. 1.
The Legionella genus harbors nine core effectors. A. The L. pneumophila wild-type strain JR32 (gray bars) and the icmT deletion mutant GS3011 (white bars) harboring the CyaA fusion proteins (indicated below each bar) were used to infect HL-60-derived human macrophages, and the cAMP levels of the infected cells were determined. Vector control is indicated as “vec.”. The bar heights represent the mean amounts of cAMP per well obtained in at least three independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations. The cAMP levels of each fusion were found to be significantly different (*, P < 0.01, Student's t-test) between the wild-type strain and the icmT deletion mutant. The effectors were examined by Western blot analysis for their expression in the wild-type strain (left) and the icmT deletion mutant (right) using an anti-CyaA antibody. B. Domain architecture of L. pneumophila core effectors orthologs. The known domains of each effector are shown. The domains presented are as follows: AcT - N-acetyltransferase; Ank, ankyrin repeat; Sel1 – Sel1 repeat, which represents a subfamily of tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR); Fe – iron binding domain (Isaac et al., 2015); CPLD - cysteine protease-like domain (Von Dwingelo et al., 2019); CC – coiled-coil region (determined using Paircoil (Berger et al., 1995)); TM – transmembrane domains (determined using TOPCONS (Tsirigos et al., 2015)). The average percent identity and similarity (%Ident /%Sim) were determined among the orthologs in all the 59 Legionella species using BLAST all-against-all.