Fig. 8. Schematic illustration of synaptic transmission by mGluR1 PAM treatment.
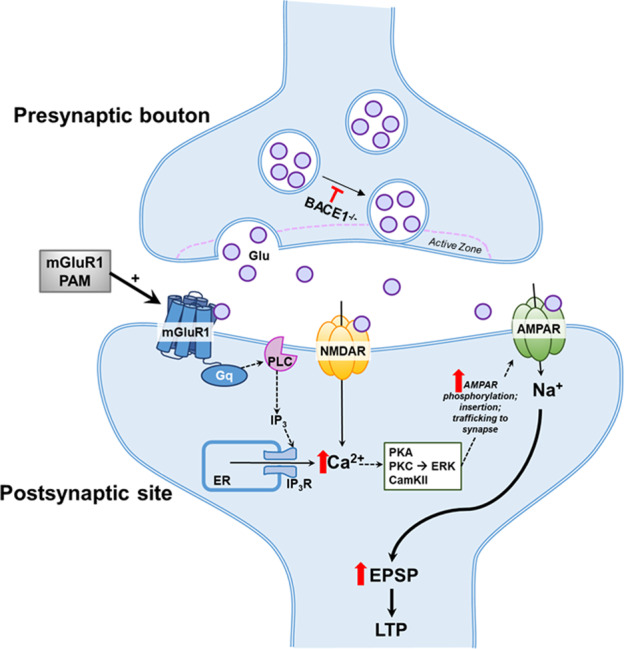
BACE1 inhibition or deficiency causes reduction in distributed of synaptic vesicles to the active zone. This causes less number of glutamate (Glu) released from these exocytosis, and weaker activation of NMDA and AMPA receptors on the postsynaptic membranes. mGluR1 PAM counteracts such a reduction by inducing more calcium (Ca2+) release through G-coupled receptor Gq-PLC-IPs pathway.
