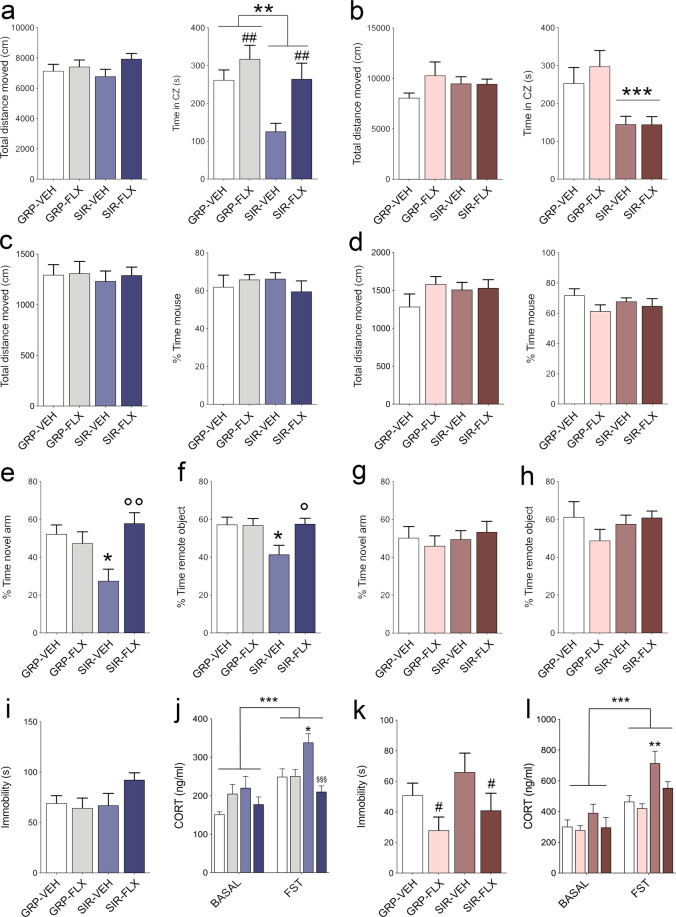
Fig. 2. Effects of maternal SIR and FLX treatment on behavior and cognition in the offspring.
a Total distance moved and time spent in the center zone of the open field test in male offspring. **p < 0.01, reflecting the main effect of SIR; ##p < 0.01, reflecting the main effect of FLX treatment. b Total distance moved and time spent in the center zone of the open field test in female offspring. ***p < 0.001, reflecting the main effect of SIR. c Total distance moved and percent exploration time of an unfamiliar mouse compared to a dummy object in the social interaction test in male offspring. d Total distance moved and percent exploration time of an unfamiliar mouse compared to a dummy object in the social interaction test in female offspring. e Relative exploration time (%) of the novel arm in the Y-maze test of spatial recognition memory in male offspring. °°p < 0.01 between SIR-VEH and SIR-FLX; *p < 0.05 between SIR-VEH and GRP-VEH. f Relative time (%) spent exploring the remote object in the temporal order memory test in male offspring; °p < 0.05 between SIR-VEH and SIR-FLX; *p < 0.05 between SIR-VEH and GRP-VEH. g Relative exploration time (%) of the novel arm in the Y-maze test of spatial recognition memory in female offspring. h Relative time (%) spent exploring the remote object in the temporal order memory test in female offspring. i Time spent immobile in the forced swim test (FST) test in male offspring. j Basal and FST-induced levels of CORT in male offspring. *p < 0.05 between SIR-VEH and GRP-VEH; §§§p < 0.001 between SIR-FLX vs SIR-VEH. k Time spent immobile in the forced swim test (FST) test in female offspring. #p < 0.05, reflecting the main effect of FLX treatment. l Basal and FST-induced levels of CORT in female offspring. **p < 0.01 between SIR-VEH and GRP-VEH; N = 10.11 mice per group and sex in a–h, N = 12-13 animals per group and sex in i–l. All values represent means ± s.e.m.