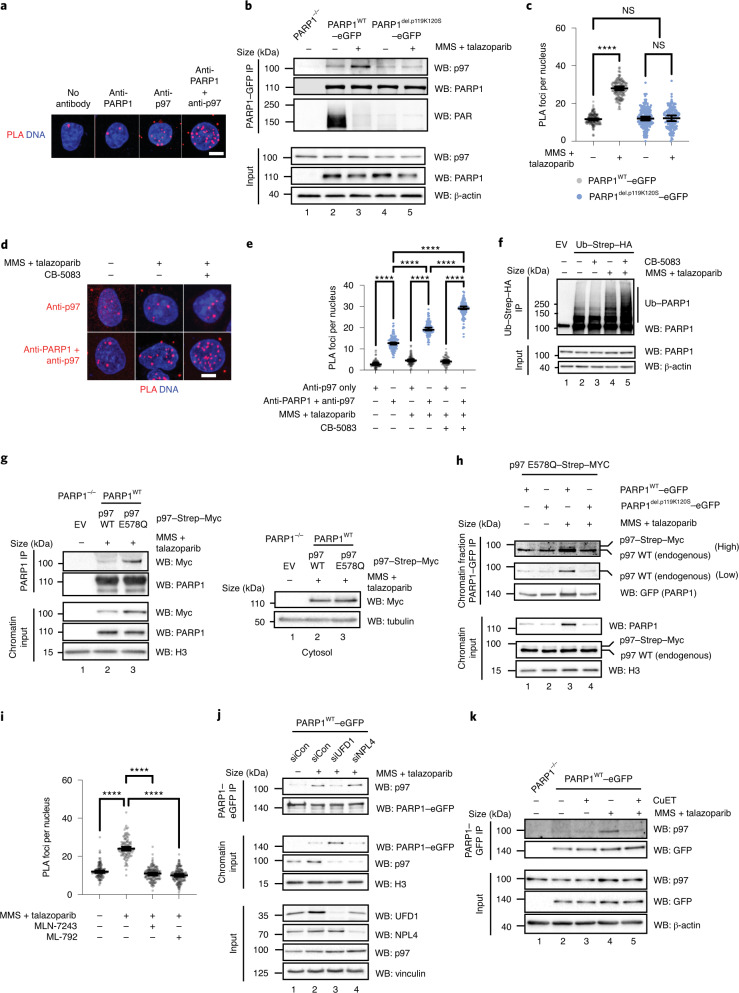
Fig. 4. PARP1 interacts with p97 in a trapping-dependent manner.
a, Images of a PLA for endogenous PARP1 and p97 in CAL51 cells. b, The PARP1–p97 interaction is increased following DNA damage. CAL51 cells expressing PARP1WT–eGFP or PARP1del.pK119S120–eGFP were exposed to trapping conditions and PARP1–GFP was immunoprecipitated under native conditions. Data represent two biological replicates. c, PARP1–p97 PLA (anti-PARP1 and anti-p97) in CAL51 cells expressing either PARP1WT–eGFP or PARP1del.pK119S120–eGFP. The geometric mean and 95% confidence interval (CI) are shown; n = 2,016 cells from three independent experiments. d, PARP1–p97 PLA in CAL51 cells under trapping. PLA with p97 antibody alone (top) or p97 + PARP1 antibody (bottom). a,d, Scale bars, 5 μm. Data represent three biological replicates. e, Number of PLA foci in d. The geometric mean and 95% CI are shown; n = 2,035 cells from three independent experiments. f, Inhibition of p97 increases the presence of ubiquitylated PARP1. HEK293 cells expressing Ub–Strep–HA were cultured in PARP1-trapping conditions in the presence or absence of 10 μM CB-5083 and the ubiquitylated proteins were immunoprecipitated under denaturing conditions (see Extended Data Fig. 6c for the input controls). Data represent three biological replicates. g, HEK293 cells expressing either wild-type p97–Myc or p97 p.E578Q–Myc were transfected with a FLAG–PARP1 construct, exposed to trapping conditions and PARP1 immunoprecipitated from the chromatin fraction. Data represent two biological replicates. h, CAL51 cells expressing PARP1WT–eGFP or PARP1del.p.119K120S–eGFP were transfected with p97 E578Q–Strep–Myc for 18 h, exposed to trapping conditions and then fractionated. The chromatin PARP1–eGFP immunoprecipitate was probed by antibody that detected both endogenous and ectopically expressed p97. Data represent two biological replicates. i, PARP1–p97 co-localization is reduced by ubiquitylation (5 μM MLN-7243) or SUMOylation (1 μM ML-792) inhibitors. Number of PARP1–p97 PLA (anti-PARP1 and anti-p97) foci. The geometric mean and 95% CI are shown; n = 1,316 cells from three independent experiments. c,e,i, ****P < 0.0001; NS, not significant; ordinary one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). j, The p97 adaptor UFD1 mediates the interaction between p97 and trapped PARP1. Chromatin-bound co-immunoprecipitation. Data represent three biological replicates; siCon, control short interfering RNA (siRNA); siUFD1, siRNA to UFD1; and siNPL4, siRNA to NPL4. k, As per j, the PARP1–p97 interaction is disrupted by the p97 sequestration agent, CuET. Data represent two biological replicates. EV, empty vector; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, western blot; and WT, wild type.