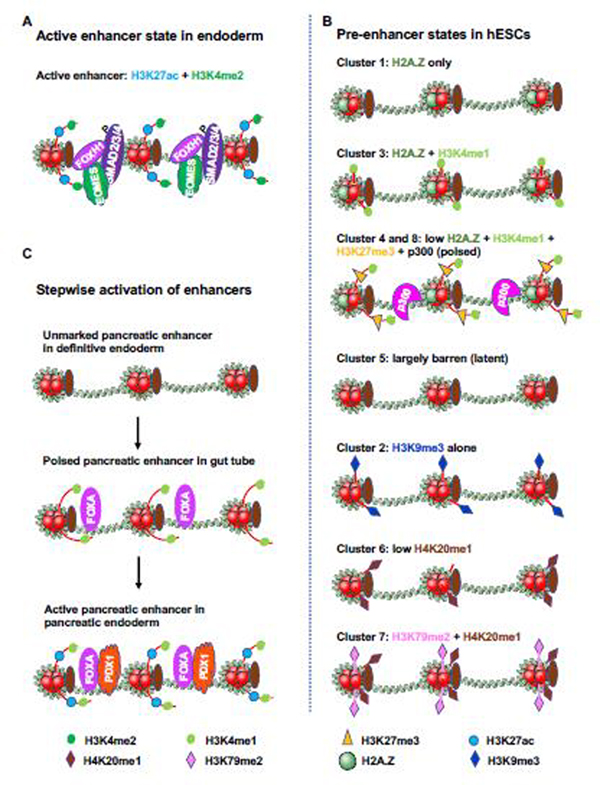
Figure 3. States of endodermal gene enhancers in hESCs and endodermal cells.
(A) Active enhancers are highly enriched for H3K27ac and H3K4me2, and are co-occupied by SMAD2/3/4, EOMES and FOXH1. The figure is adapted from [8]
(B) Chip-seq was performed in undifferentiated hESCs with chromatin marks and modifiers including H3K4me1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, H2A.Z, H3K27me3, H3K9me3, H3K27ac, H3K9ac, H3K79me2, H4K20me1, CHD1, CHD7, EZH2, HDAC2, RBBP5, JARID1A and p300. The abundance of the marks/modifiers in the future endoderm enhancers were analyzed, organized by unbiased clustering, and illustrated. The active enhancer state in endodermal cells is highly enriched for H3K27ac and H3K4me2. Cluster 4 and 8 are characterized by low H2A.Z, H3K4me1, H3K27me3 and p300, representing the “poised” enhancer state for quick activation. H2A.Z renders nucleosome unstable and facilitates transcriptional factors to bind DNA. Cluster 2 is enriched by H2A.Z and H3K4me1, marking the enhancer for subsequent activation. Those pre-enhancers are devoid of any chromatin marks/modifiers as illustrated in cluster 5, are latent in activation. The presence of multiplicity of pre-enhancer states allows a precise control of enhancer activation under the influence of both lineage inducing signals and effectors. The figure is adapted from [8].
(C) Stepwise activation of pancreatic enhancers. Pancreatic enhancers are unmarked in definitive endoderm, are poised by H3K4me1 and FOXA proteins in gut tube, and are active in pancreatic endoderm after H3K27ac deposition and PDX1 binding. The figure is adapted from [51].