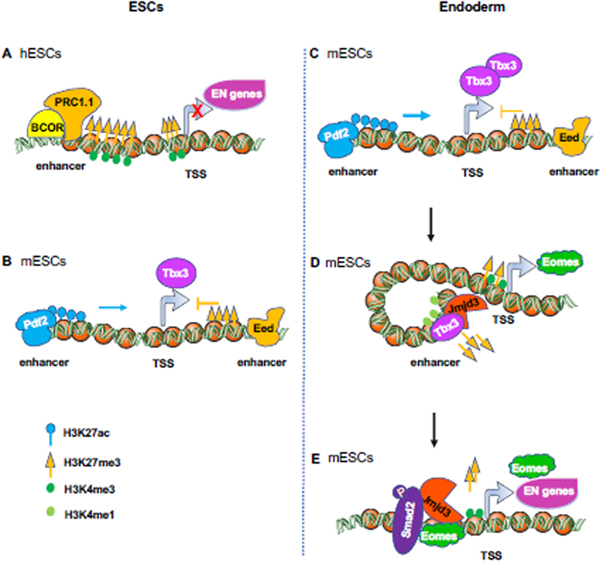
Figure 4. Dynamic regulation of H3K27 trimethylation on endodermal genes in ESCs and endodermal cells.
(A) BCOR, a member of PRC1.1 complex, specifically represses the expression of endodermal and mesodermal genes in hESCs through enhancement of H3K27me3.
(B-C) Eed and Dpf2 antagonize the expression of Tbx3 in mESCs. (B) Eed, a subunit of PRC2 complex binds an intragenic Tbx3 enhancer to oppose Dpf2 (a subunit of SWI-SNF complex)-dependent Tbx3 expression and mesendodermal differentiation in mESCs. (C) Dpf2 binds the distal enhancer of Tbx3, increases the H3K27ac level, and promotes the expression of Tbx3 during mesendodermal differentiation of mESCs.
(D-E) Jmjd3 and Eomes function in a positive feedback loop to promote endoderm differentiation from mESCs. (D) Jmjd3 physically associates with Tbx3, then binds to a bivalent enhancer (marked by H3K4me1 and H3K27me3) of Eomes, which in turn leads to a reduction of H3K27me3 deposition in the enhancer, and an interaction between enhancer and promoter, thereby promoting Eomes expression. (E) Jmjd3 and Smad2, recruited by Eomes, co-bind to the bivalent promoters (marked by H3K4me3 and H3K27me3) of core endoderm differentiation genes such as Eomes, Sox17, Gsc, Gata6, Mixl1 and Foxa2 to remove H3K27me3 for their promoter activation[48].