Figure 5.
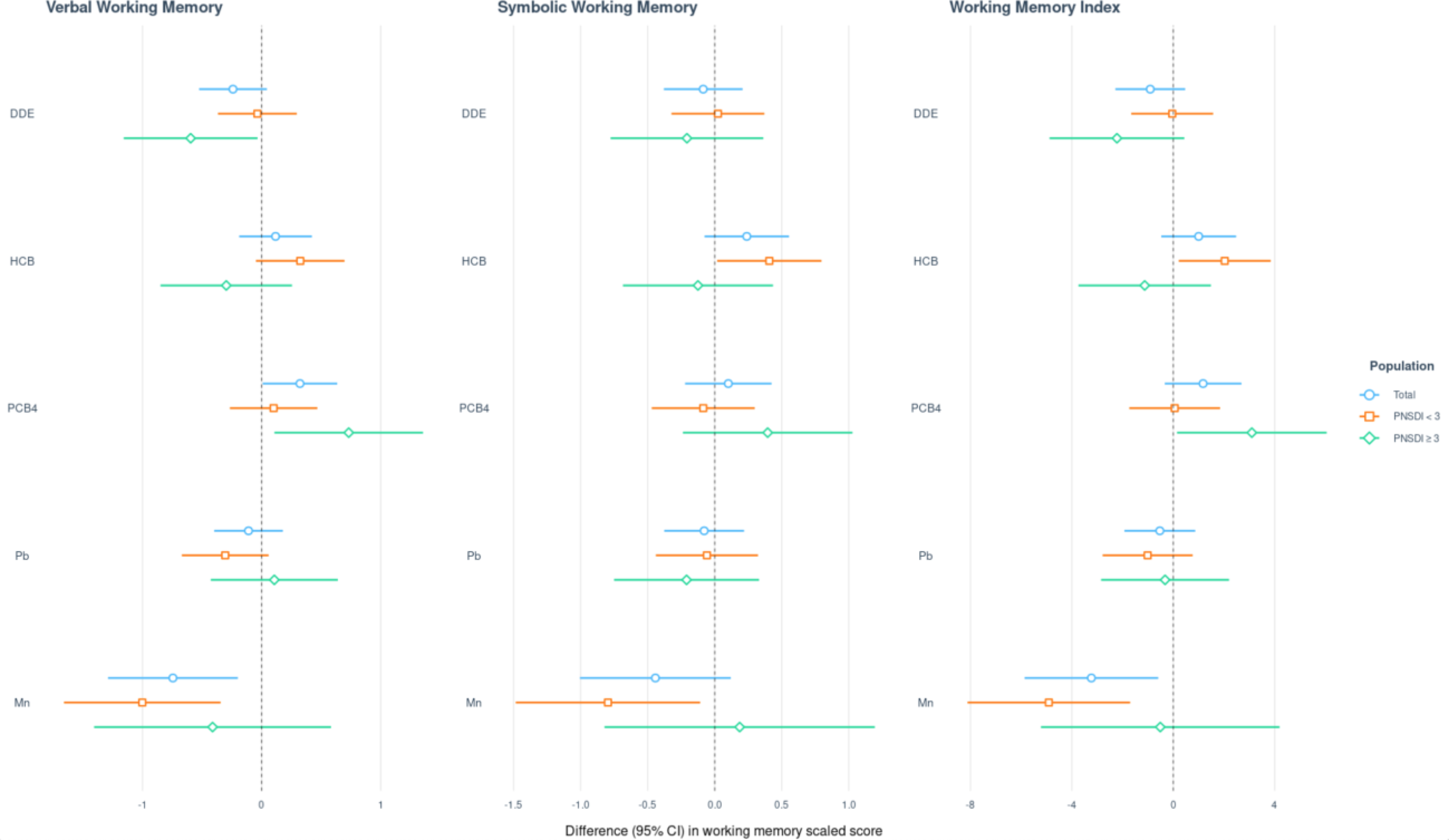
Prenatal social disadvantage index (PNSDI)1-stratified and overall results of multivariable linear regression analyses (difference in points associated with a twofold increase in exposure and 95% CI)2 assessing the relation of prenatal exposure to a five-chemical mixture with Wide Range Assessment of Memory and Learning, 2nd Edition working memory scaled scores among adolescents in the main analysis group3.
1Prenatal social disadvantage index (PNSDI) was constructed as the sum of five adverse social or economic exposures at the time of the child’s birth where presence of each risk factor was assigned a value of 1, absence a value of 0: mother unmarried, mother’s education as high school graduate or less, father’s education as high school graduate or less, annual household income less than $20,000, and mother’s age at birth less than 20 years.2Exposures have been log2-transformed and models have been adjusted for all listed exposures, child race, sex, age at exam, year of birth, and HOME score; maternal marital status at child’s birth, IQ, seafood consumption during pregnancy, and smoking during pregnancy; maternal and paternal education and annual household income at child’s birth; study examiner. 3Main analysis group: complete working memory outcome, covariate and exposure data for DDE, HCB, PCBs, Pb and Mn. Total n=373; PNSDI < 3 n= 241; PNSDI ≥ 3 n=132.
Abbreviations: DDE: dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene; HCB: hexachlorobenzene; ΣPCB4: Sum of 4 PCB congeners (118, 138, 153, 180); Pb: lead; Mn: manganese.
