Fig. 8. Summary of study.
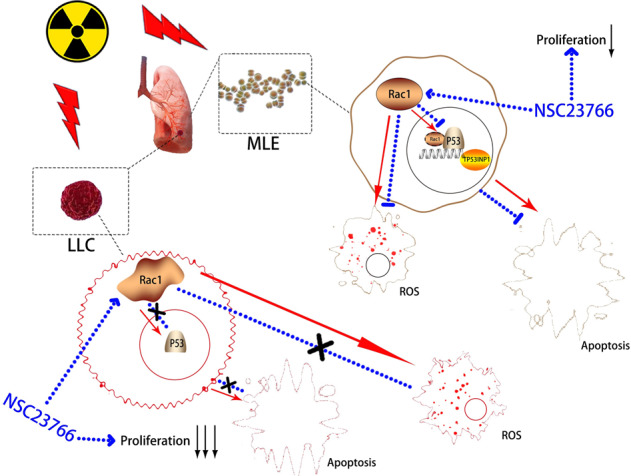
Ionizing radiation induces the nuclear translocation of Rac1, the latter then binds with p53 and prolongs the residence time of p53 in the nucleus, thereby promoting the transcription of Trp53inp1 which mediates p53-dependent apoptosis. Inhibition of Rac1 with NSC23766 could reduce the nuclear translocation of Rac1 induced by irradiation, thereby fasting the release of p53 from the nucleus, at last reducing the apoptosis. In addition, Rac1 inhibition could also significantly reduce ROS generation, but have no effect on the proliferation of MLE. In contrast, due to the overexpression and mutation of Rac1, inhibition of Rac1 does not reduce the apoptosis of tumor cells after radiation but can inhibit the proliferation ability of tumor cells significantly.
